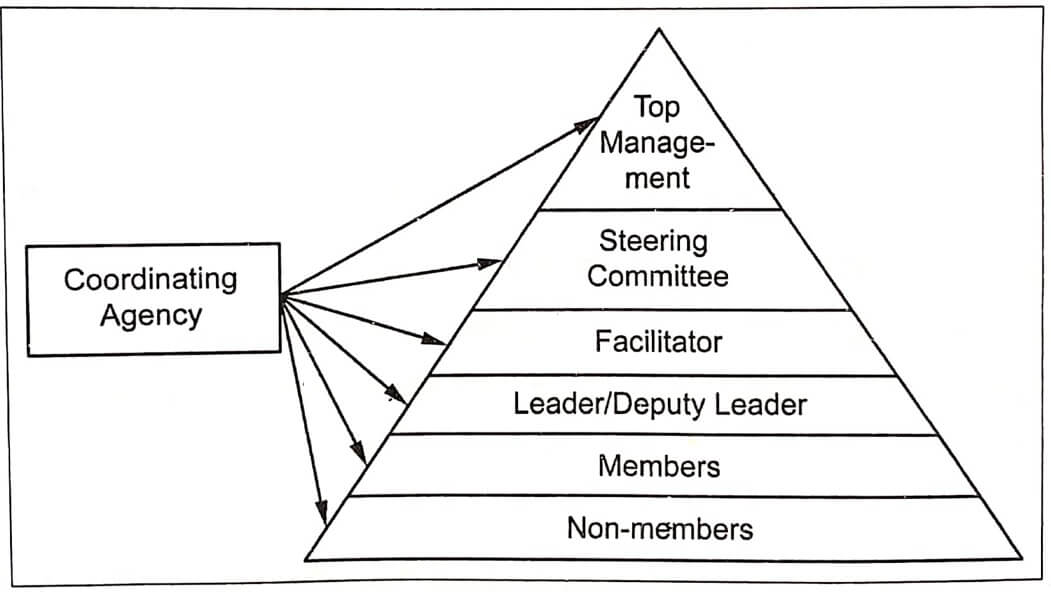
Fig .1. QC Structure
✔ A quality circle has an appropriate organizational structure for its effective and efficient performance. It varies from industry to industry, organization to organization.
✔ A typical structure of quality circle is depicted in Fig.1.
|
1.Top Management
✔ Though not directly a part of a formal quality circle structure, top-level management influences the successful implementation of the concept.
✔ A quality council collects information about the program and reports it to the Managing Director. The top management has to convey its policy of quality to its employees and encourage them to form quality circles.
✔ It should extend its support and more importantly make it visible so that even workers in the lowest level know what the top management is doing for them.
✔ It should also be lenient enough to financially support quality circle projects.
2. Coordinator
✔ A senior manager acts as a coordinator. He arranges steering committee meetings and is responsible for proper documentation of various activities.
✔ He organizes training programs whenever needed.
✔ Overall, he is responsible for conducting seminars, presentations, and case studies and publishing periodicals to ascertain that the work of the quality circle is recognized.
3. Steering committee
✔ A steering committee is a group of members working under the chairmanship of the CEO with functional heads as members.
✔ The members of steering committee are responsible for proper implementation of the quality circle in their respective areas. They make the facilitators under them accountable to them. The CEO reviews the reports of the members’ activities and makes suggestions.
4. Facilitator
✔ A senior person in a specific area acts as a facilitator. He bears the responsibility to catalyze and motivate the quality circles.
✔ He acts as a guide or mentor for effective operation of quality circles.
✔ Further, he also elucidates the functioning of quality circles in his area in steering committee meetings.
5. Leader/Deputy Leader
✔ The members of the circle chose a leader with due care and consensus. As the leader shapes the circle’s effectiveness, training him is vital.
✔ A good leader should have the ability to motivate members of the team, conduct meetings, and coordinate efforts apart from involving all the members in the quality philosophy. He should strive to avert conflicts and ensure quality-oriented teamwork.
6. Members
✔ Members of a circle should not be forced to join a quality circle, instead they should join of their own interest.
✔ They need to have an understanding of the functioning of quality circles.
✔ They should encourage other employees to participate in the movement, zealously involve themselves in the quality improvement programs, implement solutions and give presentations effectively.
7. Non-members
✔ Non-members are important because they support circle members externally.
✔ Also, if they realize the benefits of forming circles, they will willingly participate in the activities. Hence, non-members are often considered prospective members.
Though quality circles essentially comprise a small group of workers, the involvement of all the employees of an organization at some point is critical. Following a structural hierarchy will ensure a smooth flow of the circle’s activities.
|
1.Roles of Quality Circle Members
|
|
2. Roles of Quality Circle Leader
|
|
3. Roles of Facilatator
|
|
4. Roles of Steering Committee
|
|
5. Roles of Coordinator
|