In Hysteresis, after a cycle of magnetization, there is some expenditure (loss) of energy. This loss of energy is radiated in the form of heat energy in the material and it is directly proportional to the area of the loop. From the Hysteresis graph, we can select the soft and hard magnetic materials .
Hard Magnetic Materials
Hard magnetic materials are the materials which are very difficult to magnetize and demagnetize. These materials can be made by heating the magnetic materials and then suddenly cooled. Also it can be prepared by adding impurities.
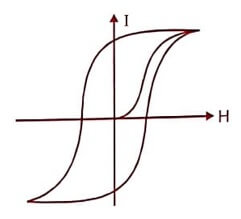
Fig : (1) Hysteresis loop of a hard magnetic material
- The above hysteresis loop is very broad and has a large loop area for a hard magnetic material. Therefore the loss is also large.
- Domain wall does not move easily and require large value of H for magnetisation.
- Its coercivity and retentivity values are large.
- Its eddy current loss is also high due to its low resistivity.
- The magnetostatic energy is large.
- It has low susceptibility and permeability.
- The hard magnetic materials have large amount of impurities and lattice defects.
- Example: Tungsten steel, Carbon steel, Chromium steel, Cunife, Cunico, Alnico etc.,
- It is used to produce permanent magnets, DC motor magnets, etc.,
Soft Magnetic Materials
Hard magnetic materials are the materials which are easily magnetized and demagnetized. These materials can be made by heating the magnetic materials and then slowly cooled to attain an ordered structure of atoms.
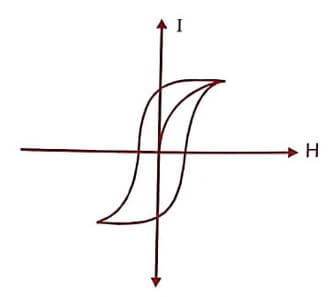
Fig : (1) Hysteresis loop of a soft magnetic material
- The above hysteresis loop is very small and has a less loop area for a soft magnetic material. Therefore the loss is also small.
- Domain wall move easily and require small value of H for magnetisation.
- Its coercivity and retentivity values are small.
- Its eddy current loss is small due to its high resistivity
- The magnetostatic energy is less.
- It has high value of susceptibility and permeability.
- The soft magnetic materials do not have impurities and lattice defects.
- Examples: Iron-Silicon alloys, Nickel-Iron alloys and Ironcobalt alloys.
- It is used to produce Electro magnets, computer data storage, Transformer core, etc.,
Difference between Hard and soft magnetic materials
| S. No | Hard Magnetic Materials | Soft Magnetic Materials |
| 1. | Cannot be easily magnetised | Can be easily magnetised |
| 2. | It can be produced by heating and sudden cooling | It can be produced by heating and slow cooling |
| 3. | Domain wall does not move easily and require large value of H for magnetisation | Domain wall move easily and require small value of H for magnetisation |
| 4. | Hysteresis loop area is large. | Hysteresis loop area is small. |
| 5. | Susceptibility and permeability values are high. | Susceptibility and permeability values are less. |
| 6. | Retentivity and coercivity are large. | Retentivity and coercivity are small. |
| 7. | High eddy current loss. | Low eddy current loss. |
| 8. | Impurities and defects will be more. | No Impurities and defects. |
| Example: Tungsten steel, Carbon steel, Chromium steel, Cunife, Cunico, Alnico.
Uses: Permanent magnets, DC motor magnets |
Examples: Iron-Silicon alloys, Ferrous Nickel alloy Ferrites, Garnets.
Uses : Electro magnets, computer data storage, Transformer core |
| Read More Topics |
| Elemental and compound semiconductor |
| Mobility and conductivity in semiconductors |
| Electrical conductivity in intrinsic semiconductor |





