The cells used for electrolysis are called electrolytic cells while those used for generation of electrical energy from chemical reactions are called galvanic or voltaic cells.
The practical application of a galvanic cell is Daniel cell. The electrode where oxidation occurs is called anode and the electrode where reduction occurs is called cathode.
John Daniell (English physicist) developed the first modern storage cell based on Faraday’s principles.
Construction
The Daniel cell consists of the following two half cells: (a) zinc electrode dipped in ZnSO4 solution and (b) copper electrode dipped in CuSO4 solution.
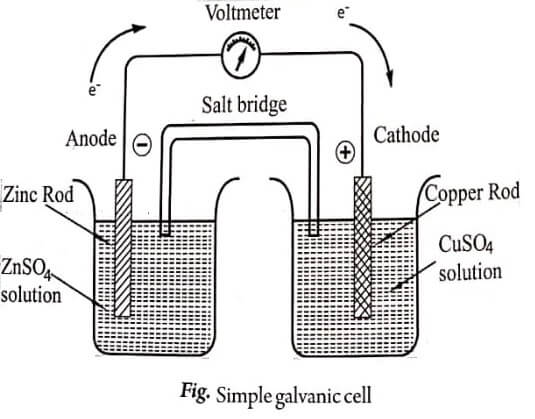
The solutions of the half cells are connected by a salt bridge (salt bridge is an inverted U tube containing KCl or KNO3 (or) NH4NO3 saturated solution taken in agar-agar/ gelatin) and the electrodes are connected by means of a metallic conductor (wire) and a voltmeter to measure the potential.
Working
The electrode reaction of Daniel cell is given below:
Zinc rod slowly dissolves in the solution to form Zn2+ ions (i.e.,) zinc behaves as anode; oxidation takes place and the reaction can be given as,
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e– (at anode)
and the anode half cell can be represented as Zn/Zn2+
Cu2+ ions move from solution and get deposited over the copper rod i.e., copper behaves as cathode; reduction takes place and the reaction can be given as,
Cu2+(aq) + 2e− ⟶ Cu(s) (at cathode)
and the cathode half cell can be represented as Cu2+ / Cu. Thus the flow of electrons from Zn rod to Cu rod.
The overall cell reaction is
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
and the emf of the cell is V.
Representation of a galvanic cell
A cell diagram or a cell representation is an abbreviated symbolic representation of an electrochemical cell. For representing a cell, a set of IUPAC conventions should be followed.
- The anode half cell is written on the left-hand side and cathode half cell on the right-hand side while formulating a galvanic cell.
- While writing the anode half cell, the metal is written first and then the metal ion. For the cathode half cell, the metal ion is written first and then the metal.
- A single vertical line represents the boundary between different phases that constitute an electrode.
- While writing the metal ion either the whole formula of electrolyte or as metal ion species can be given also indicating the concentration within brackets. So anode half cell is represented as, Zn / Zn2+ (IM) (or) Zn / ZnSO4 (IM) and the cathode half cell is represented as, CU2+ (IM) /Cu (or) CuSO4 (IM) /Cu.
- The two half cells will be separated by a double vertical line denoting the salt bridge/porous partition or any other means of permitting only the ionic flow.
So, the complete cell representation of Daniel cell can be given as
Zn/Zn2+ (IM) // Cu2+ (IM) / Cu (or) Zn / ZnSO4 (IM) // CuSO4 IIM) / Cu.
| Read More Topics |
| How do sodium potassium pumps work |
| Types of softening of water processes |
| What is a redox reaction? |





