✔ The word ‘benchmark’ is a reference or measurement standard used for comparison. Benchmarking is the process of determining who is the very best, who sets the standard, and what that standard is.
✔ Benchmarks and benchmarking can provide the answers to the following questions of an organisation: “How are we doing?”; “How do we compare with others?”: “Are we tracking the right measures?”; “Are we making progress fast enough?” “Are we using the best practices?”.
✔ Benchmarking can provide them with data to show what can be achieved and how can be achieved.
✔ Definition: Benchmarking is a systematic method by which organisations can measure themselves against the best industry practices.
✔ In more conventional terms, benchmarking can be defined as measuring an organisation’s performance against that of best-in-class companies, determining how the best-in-class achieve those performance levels.
✔ The essence of benchmarking is the process of barrowing ideas and adapting them to gain competitive advantage. Therefore it is a tool for continuous improvement.
Benchmarking: What is it?
✔ American Productivity and Quality Centre (APQC) has defined the benchmarking as the process of identifying, understanding, and adapting outstanding practices and processes from organisations anywhere in the world to an organisation to improve its performance.
✔ David Kearns defines benchmarking as “the continuous process of measuring products, services and practices against the toughest competitors or those companies recognised as industry leaders.
✔ Thore defines benchmarking as “the systematic comparison of elements of performance of an organisation against those of other organisations, usually with the aim of mutual improvement.”
Benchmarking concept: The concept of benchmarking is illustrated in Fig.1.
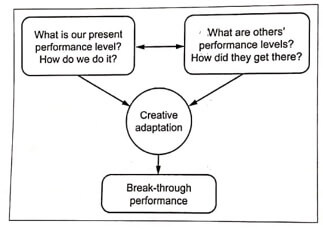
Fig.1. Benchmarking concept
Reasons to Benchmark (Objectives of Benchmarking)
- Benchmarking aims at a goal setting process to facilitate comparison with the best.
- It aims at motivating and stimulating company employees towards the goal of continuous quality improvement.
- It aims at external orientation of the company.
- It aims at identifying a technological break-through.
- It aims at searching for industry best practices.
Table 10.1 highlights the various reasons for carrying out benchmarking.
| Objectives | Without benchmarking | With benchmarking |
| Becoming competitive |
|
|
| Industry best practices |
|
|
| Defining customer requirements |
|
|
| Establishing effective goals and objectives |
|
|
| Developing true measures of productivity |
|
|