Human Anatomy is the study of the structures of living organisms, focusing on how their bodies are built and function. It’s a key branch of both biology and medicine.
The origins of anatomy date back over 2,000 years to Ancient Greece. The field has three main areas: human anatomy, animal anatomy (known as zootomy), and plant anatomy (called phytotomy).
The word “anatomy” originates from the Greek words “ana,” which means “up,” and “tome,” which means “a cutting.” Historically, studying anatomy involved cutting open or dissecting organisms to understand their structures.
In this blog, we have reviewed why human anatomy is essential for those who want to pursue a career in microbiology.
Gross Human Anatomy
In medicine, gross anatomy (macroscopic or topographical anatomy) is the study of visible biological structures. You don’t need a microscope to observe them.
A dissection scientist opens up an organism, whether a plant, human, or animal, to study its internal structures. For example, a doctor or scientist passes a thin, flexible tube with a camera through the mouth or rectum into the body to inspect the inside of the gastrointestinal portion.
MRI scans, CT scans, PET scans, X-rays, ultrasounds, and other imaging methods can also show the internal structure of a living body. Moreover, medical and dental students perform dissections for their practicals.
Body Systems
The human body consists of different systems, including the skeletal, muscular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, nervous (central and autonomic), endocrine (hormone regulation), cardiovascular (heart and blood vessels), urinary, reproductive, and integumentary (skin, hair, nails) systems. Gross anatomy students study these 11 major organ systems of a body.
Microscopic Anatomy
Microscopic anatomy, or histology, focuses on small cells and tissues in animals, humans, and plants that cannot be seen without a microscope.
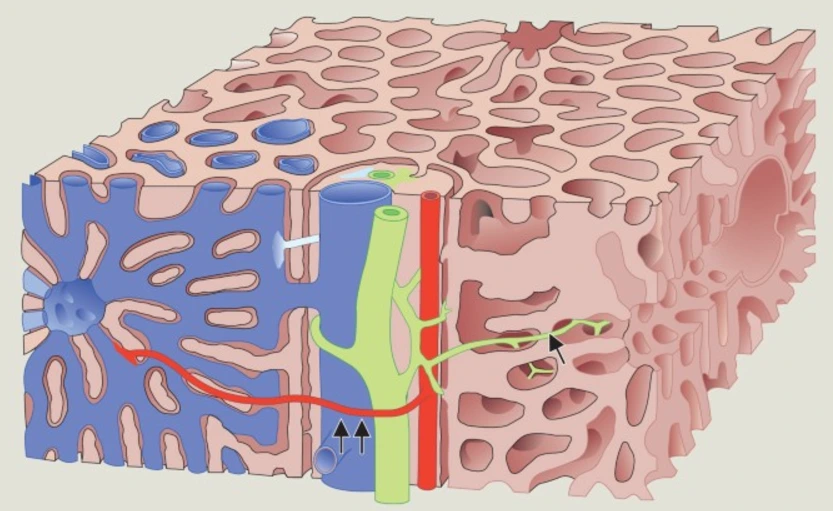
Microscopic anatomy helps us understand the structure of cells and how they interact. For example, when examining tissue under a microscope, doctors can observe how cancerous cells behave and how they impact healthy tissue.
A researcher can also use sectioning and staining histological methods on tissues and cells to study them under a light or electron microscope.
Scientists use histology for different purposes, including:
- Teaching: In labs, histology slides help students explore the microstructures of biological tissues.
- Diagnosis: Doctors collect tissue samples, or biopsies, from patients suspected of cancer or other illnesses and send them to a lab for a histologist’s analysis.
- Forensic investigations: If a person dies suddenly, the microscopic examination of specific tissues can help experts explore the root cause.
Histopathology
Those who work in histology labs are known as histotechnicians, histotechnologists, or histology technicians. They prepare the analysis samples, while histopathologists, or pathologists, study and interpret these samples.
A histopathologist then studies cells and tissues and explains the findings. Their results help others find the best treatment options or analyze the reason for death, illness, or crime.
Anatomy Training
Most healthcare professionals, including paramedics, nurses, physical and occupational therapists, doctors, prosthetists, and biological scientists, are trained in gross anatomy and histology for their practicals.
In conclusion, understanding human anatomy is essential for microbiology students, as it helps them know how the human body functions and how diseases affect it. Students learn about the body’s visible structures (gross anatomy), the microscopic details of cells and tissues (microscopic anatomy or histology), and the intricate systems that work together to keep us healthy.
Moreover, Human anatomy plays a key role in medicine and healthcare, helping professionals diagnose illnesses, plan treatments, and solve forensic cases. For microbiology students, a strong base in anatomy is not only academic but an essential step toward making confidential contributions to science and improving human health.