No, you cannot directly use a SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) cable with a SATA (Serial ATA) drive because SAS and SATA are different storage interfaces. However, SAS controllers are designed to support both SAS and SATA drives, meaning a SATA drive can connect to a SAS controller, but a SAS drive cannot connect to a SATA controller.
When it comes to storage interfaces, SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) and SATA (Serial ATA) are two of the most common technologies used today. These interfaces are crucial for connecting hard drives, SSDs, and other storage devices to computers or servers. But one common question that comes up is, “Can I use a SAS cable for a SATA drive?” Let’s dive deep into this question and explore the ins and outs of SAS and SATA, their compatibility, and what you need to know before connecting them.
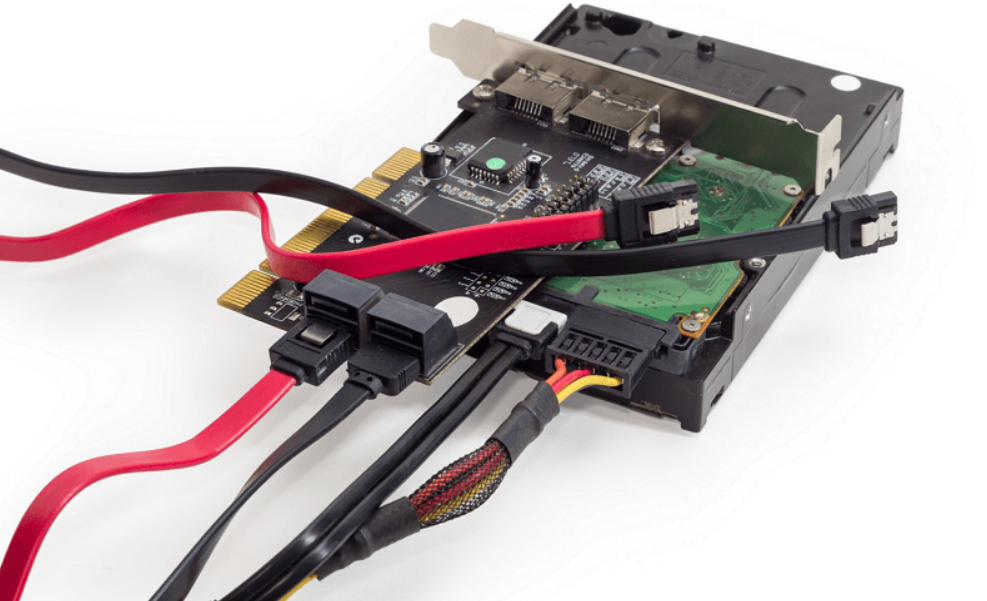
[sc_fs_faq html=”true” headline=”h2″ img=”” question=”What is a SAS Cable?” img_alt=”” css_class=””] A SAS cable is a high-speed data cable used to connect storage devices to a host bus adapter or RAID controller, primarily in enterprise environments. SAS cables are designed for Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) technology, a more advanced and scalable storage protocol compared to older parallel SCSI systems. [/sc_fs_faq]
SAS cables typically come with multiple lanes, allowing for higher data throughput and improved fault tolerance. These cables are commonly found in servers, data centers, and enterprise-grade storage solutions due to their reliability and high-speed capabilities.
What is a SATA Drive?
A SATA drive is a type of storage device that uses the SATA interface to connect to a computer or other systems. SATA drives can be either hard disk drives (HDDs) or solid-state drives (SSDs). They are popular among consumers and businesses due to their affordability and relatively good performance.
There are three generations of SATA, with SATA 3 being the latest and fastest, offering data transfer speeds of up to 6 Gb/s. SATA drives are most commonly used in personal computers, laptops, and small servers.
Differences Between SAS and SATA
Speed Comparison: One of the primary differences between SAS and SATA lies in speed. While SATA drives max out at 6 Gb/s, SAS drives can achieve speeds up to 12 Gb/s, depending on the version. Additionally, SAS controllers often handle multiple data lanes, further increasing their total bandwidth.
Data Integrity and Reliability: SAS drives are designed for environments where data integrity is critical, such as enterprise data centers. They come with better error correction, dual-port capabilities, and support for hot-swapping. SATA, on the other hand, is more suited for general consumer use, where data integrity and redundancy are less of a priority.
Performance in Enterprise vs. Consumer Environments
SAS drives tend to perform better in enterprise environments where multiple users access data concurrently. In contrast, SATA drives are well-suited for consumer-grade applications where affordability is more important than top-tier performance.
Are SAS and SATA Compatible?
Physical Compatibility: Physically, SAS connectors are designed to be backward-compatible with SATA drives. This means that a SAS controller can accept a SATA drive connection. However, the reverse is not true; you cannot connect a SAS drive to a SATA controller.
Electrical and Data Compatibility: While the physical connection works, SAS and SATA use different protocols for data transfer. However, SAS controllers are typically designed to handle both SAS and SATA drives, allowing for mixed environments where both types of drives coexist.
Can You Use a SAS Cable for a SATA Drive?
Yes, you can use a SAS cable to connect a SATA drive to a SAS controller. The reason this works is that SAS controllers are designed to be backward-compatible with SATA. This means that a SATA drive can communicate with a SAS controller, but only at SATA speeds.
However, using a SAS cable for a SATA drive has its limitations. SATA drives will not take full advantage of the SAS interface’s higher speed and advanced features, such as multiple lanes and improved error correction.
How to Connect a SATA Drive to a SAS Controller
- Gather your tools: You’ll need a SAS cable, a SAS controller, and a compatible SATA drive.
- Insert the SATA drive: Connect the SATA drive to the SAS controller using a SAS cable.
- Check connections: Ensure everything is firmly connected and seated properly.
- Power up: Boot your system and check if the drive is recognized.
Conclusion: While you can use a SAS cable for a SATA drive, there are trade-offs in terms of performance. SAS controllers are backward-compatible with SATA, but the benefits of SAS, such as higher speed and better data integrity, are not fully realized when using SATA drives. Understanding the differences between SAS and SATA can help you make the right choice based on your storage needs.
| Read More Topics |
| Definition and origin of electrode potential |
| Three types of optical fibre |
| Photonics introduction and properties of laser |