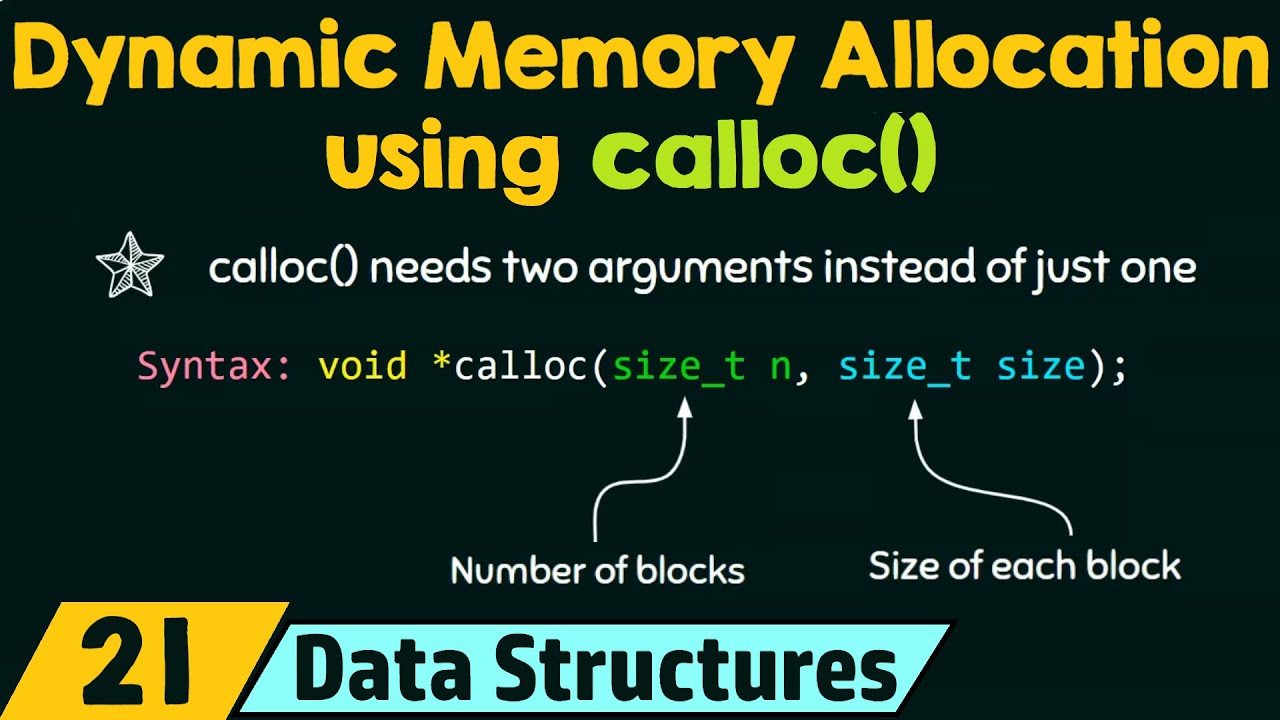
calloc in c is another memory allocation function that is normally used for requesting memory space at run time for storing derived data types such as arrays and structures. While malloc allocates a single block of storage space, calloc in c allocates multiple blocks of storage, each of the same size, and then sets all bytes to zero. The general form of calloc is
ptr = (cast-type *) calloc (n, elem-size);
The above statement allocates contiguous space for n blocks, each of size elem-size bytes. All bytes are initialized to zero and a pointer to the first byte of the allocated region is returned. If there is not enough space, a NULL pointer is returned.
The following segment of a program allocates space for a structure variable:
…..
…..
struct student
{
char name[25];
float age;
long int id_num;
};
typedef struct student record;
record *st_ptr;
int class_size = 30;
st_ptr=(record *)calloc(class_size, sizeof (record));
…..
…..
record is of type struct student having three members: name, age and id_num. The calloc in c allocates memory to hold data for such records. We must be sure that the requested memory has been allocated successfully before using the st_ptr. This may be done as follows:
if(st_ptr == NULL)
{
printf(“Available memory not sufficient”);
exit(1);
}
The calloc() function in C is used to allocate a specified of memory and then initialize it to zero.
| Read More Topics |
| Additional Features of SQL |
| Insert, Delete, and Update Statements in SQL |
| SQL Data Definition and Data Types |
| Relational Model Concepts in DBMS |