Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain Methods (Image Plane)
-
- Techniques are based on direct manipulation of pixels in an image
- Frequency Domain Methods
- Techniques are based on modifying the Fourier transform of the image.
- Combination Methods
- There are some image enhancement in spatial domain techniques based on various combinations of methods from the first two categories
Statistical Order/Non-Linear Filters
Some simple neighbourhood operations include:
Min: Set the pixel value to the minimum in the neighbourhood
Max: Set the pixel value to the maximum in the neighbourhood
Median: The median value of a set of numbers is the midpoint value in that set (e.g. from the set [1, 7, 15, 18, 24] 15 is the median). Sometimes the median works better than the average
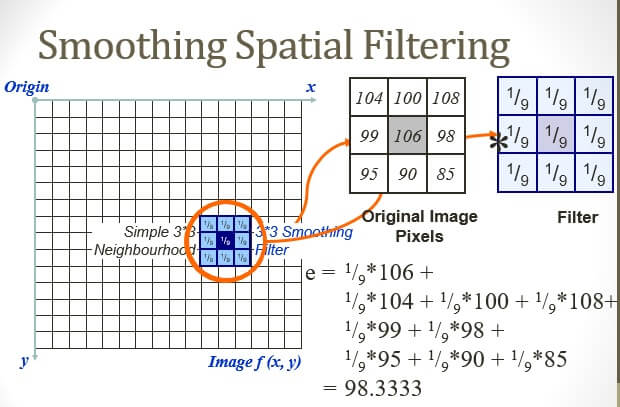
Smoothing Spatial Filters
- One of the simplest spatial filtering operations we can perform is a smoothing operation
- Simply average all of the pixels in a neighbourhood around a central value
- Especially useful in removing noise from images
- Also useful for highlighting gross detail
Image Smoothing Example

- The image at the top left is an original image of size 500*500 pixels
- The subsequent images show the image after filtering with an averaging filter of increasing sizes
- 3, 5, 9, 15 and 35
- Notice how detail begins to disappear
Weighted Smoothing Filters
- More effective smoothing filters can be generated by allowing different pixels in the neighbourhood different weights in the averaging function
- Pixels closer to the central pixel are more important
- Often referred to as a weighted averaging
- By smoothing the original image we get rid of lots of the finer detail which leaves only the gross features for thresholding
Averaging Filter Vs Median Filter Example
- Filtering is often used to remove noise from images
- Sometimes a median filter works better than an averaging filter
Strange Things Happen At The Edges!
- There are a few approaches to dealing with missing edge pixels:
- Omit missing pixels
- Only works with some filters
- Can add extra code and slow down processing
- Pad the image
- Typically with either all white or all black pixels
- Replicate border pixels
- Truncate the image
- Allow pixels wrap around the image
- Can cause some strange image artifacts.
| Read More Topics |
| Image Processing Digital and Analog |
| Function of layer in OSI model |
| Decision making and branching in C |