Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disorder, in which antibodies are produced at neuromuscular junction (NMJ) against the NM receptors, so, it results in decrease in the number of NM receptors. Patients with myasthenia gravis show severe muscular weakness. The degree and intensity may vary at different times.
Patients with thymoma show an increased risk of development of myasthenia gravis.
MG can be diagnosed by the following methods:
Typical Signs and Symptoms : The typical signs and symptoms of myasthenia gravis include:
- Diplopia,
- Ptosis,
- Dysarthria,
- Weakness in chewing,
- Dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing),
- Muscle weakness of limbs with preserved deep tendon reflexes,
- Weakness of neck flexion and more rarely extension,
- Weakness of trunk muscles,
- Respiratory symptoms with respiratory failure, and
- Increased weakness during exercise and repetitive muscle use with at least partially restored strength after periods of rest.
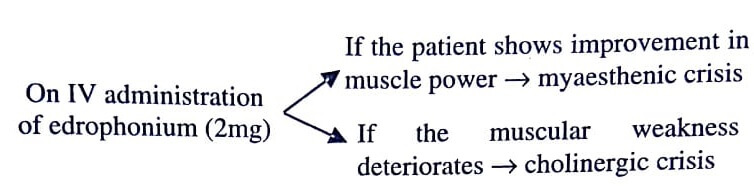
Edrophonium Test : This test is used to distinguish between patients affected with myasthenia gravis and those affected with other muscular dystrophies. Slow administration of edrophonium (a short-acting acetylcholinesterase inhibitor) in doses ranging from 2−10mg shows a significant improvement by causing reversibility of muscle weakness in patients with myasthenia gravis.
Antibody Test : Detection of circulating antibodies to NM receptors like anti-AChR antibodies, antiMuSK antibodies, anti-striational antibodies.
Neurophysiological Tests : Repetitive Nerve Stimulation (RNS) and Single Fibre Electromyography (SFEMG) are most commonly used for neurophysiological tests.
MG can be treated by :
Modulation of Neuromuscular Transmission : The neuromuscular transmission is modulated by administration of anticholinesterases (cholinesterase inhibitors) such as pyridostigmine bromide (Mestinon) and neostigmine bromide (Prostigmin).
Immunomodulation : Modulation of the immune system is brought about by :
- Plasma Exchange: It helps to remove abnormal antibodies.
- Intravenous Immune Globulin (IVIG): It brings about down-regulation of antibodies directed against AChR.
- Immunoadsorption: This procedure helps to remove anti-AChR antibodies.
Immunosuppression : Corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone) and other immunosuppressants like azathioprine, cyclosporin, mycophenolate mofetil, and tacrolimus can be used to suppress the immune system, thus, suppressing the production of abnormal antibodies.
Drugs like aminoglycoside antibiotics, d-tubocurarine (d-TC) and other neuromuscular blockers, β-blockers, ether, phenytoin, etc., should not be used as they aggravate myasthenia and are hence contraindicated.
| Read More Topics |
| Steps in neurohumoral transmission |
| Function of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) |
| Transmembrane enzyme linked receptors |
| Plasma protein binding of drug |






