Definition : If the interaction among permanent dipoles is strong such that all the dipoles line up in parallel, the material is Ferromagnetic.
or
The substances which when placed in a magnetic field are strongly magnetised in the direction of applied magnetic field are called ferromagnetic materials.
Examples: Nickel (Ni), Cobalt (Co), Iron (Fe), etc.,
Explanation :
In this Ferromagnetic materials, the net spin magnetic moment are of the same order as that of a paramagnetic materials, still exhibits strong magnetisation.
This is due to the spontaneous magnetisation. This occurs due to a special form of interaction called exchange coupling between adjacent atoms even in the absence of applied magnetic field coupling their magnetic moments together in rigid parallelism.
When placed in a magnetic field it strongly attracts the magnetic lines of forces and the substance becomes magnetized. The transition metals like Ni, Fe and Co exhibit magnetism even when the magnetic field is removed.
It has a characteristic temperature called the ferromagnetic curie temperature (θF) . The permeability depends greatly on temperature.
The temperature above which the ferromagnetic materials behaves as a paramagnetic material and below which behaves as ferromagnetic material is called ferromagnetic Curie temperature.
In ferromagnetic materials, the magnetic dipoles are arranged parallel to each other (Fig). These materials consists of number of small regions called domains which are spontaneously magnetized.
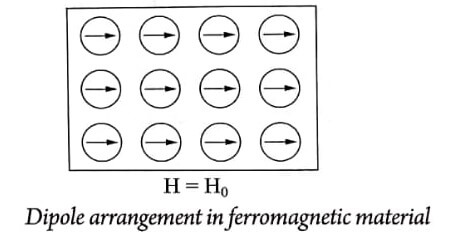
Properties
- They have permanent dipole moment.
- It is strongly attracted by a magnet.
- They exhibit magnetisation even in the absence of external field. This property is called Spontaneous magnetization.
- Since some magnetisation is already existing in these materials, all the magnetic lines of force passes through it.
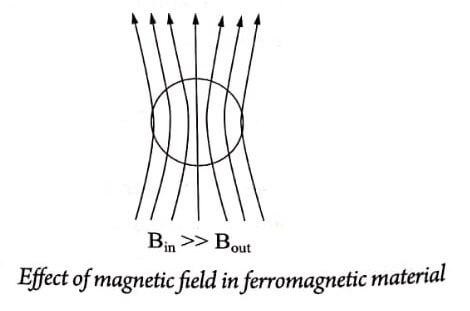
5. It’s susceptibility is positive and high. Also it depends on temeperature. Fig.
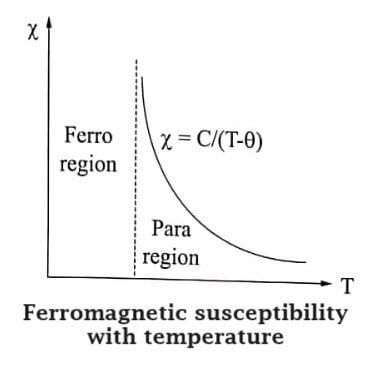
6. When the temperature is greater than curie temperature, ferromagnetic materials becomes paramagnetic material.
7. Permeability is very much greater than 1.
8. They exhibit magnetization even when the magnetizing field is removed. Hence they exhibit magnetic hysteresis.
9. If a ferromagnetic substance is placed in a nonuniform magnetic field, it is attracted towards the stronger magnetic field.
10. They consists of number of small regions which are spontaneously magnetised. These small regions are called domains.
11. Spin alignment of adjacent dipoles is parallel to each other along the same direction.
| Read More Topics |
| Definition and properties for paramagnetism |
| Definition and properties for diamagnetism |
| Classification of magnetic materials |





