1. A paramagnetic material has a magnetic field intensity of 104 Am-1. If the susceptibility of the material at room temperature is 3.7×10-3. Calculate the magnetization and flux density in the material.
Given
H = 104 A m-1, χ = 3.7 × 10-3, I =?, B = ?
Solution:-
(i) 
(ii) 
2. A magnetic material has a magnetization of 2300 Am−1 and produces a flux density of 0.00314 Wb m−2. Calculate the magnetizing force and the relative permeability of the material.
Given
I = 23000 Am-1, B = 0.00314Wb m-2, H =?, μr = ?
Solution:-
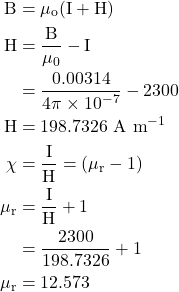
μr = 12.573
3. A paramagnetic material has BCC structure with a cubic edge of 2.5 A°. If the saturation value of magnetization is 1.8×106 Am−1, Calculate the magnetization contributed per atom in Bohr magnetons.
Given
a = 2.5 × 10-10 m, I = 1.8×106 Am-1, MT = ?
Solution:-
The number of atoms present per unit volume

The magnetization produced per atom ![]()
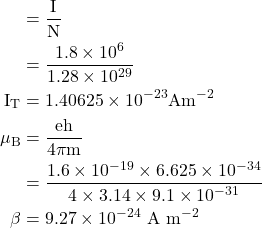
∴ Magnetisation produced per atom in Bohr magneton

4. The saturation magnetic induction of Nickel is 0.65 Wb m−2. If the density of Nickel is 8906 Kg m−3 and its atomic weight is 58.7. Calculate the magnetic moment of the Nickel atom in Bohr magneton.
Given
Bs = 0.65 Wb m-2, ρ = 8906 Kg m-3, Atomic Weight = 58.7, μm = ?
Solution:-

When χ is very large, Saturation magnetization

Magnetic moment per Bohr magneton
![]() Bohr magneton
Bohr magneton
μm = 0.61 μB
5. In a magnetic material the field strength is found to be 106 Am−1. If the magnetic susceptibility of the material is 0.5×10−5. Calculate the intensity of magnetization and flux density in the material.
Given
H = 106 Am-1, χ = 0.5 × 10-5, B = ?, I = ?
Solution:-
(i) I = χH
= 0.5 × 106 × 10-5
I = 5 A m-1
(ii) B = μ0 (I + H)
= 4 × 3.14 × 10-7 (5 + 106)
B = 1.257 Wbm-2
6. The critical temperature of Niobium is 9.15 K. At 0K the critical field is 0.196 T. Calculate the critical field at 5 K.
Given
Tc = 9.15 K, T = 5 K, H0 = 0.196 T, HC = ?
Solution:-
![]()
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{aligned} & =0.196\left[1-\frac{5^2}{9.15^2}\right] \\ & =0.196 \times 0.7014 \\ c_c & =\mathrm{OH} 374 \text { Tesla } \end{aligned}](https://pedagogyzone.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-594798e7548735830b4d7d08129e9df4_l3.png)
7. Calculate the critical current through a long thin superconducting wire of radius 0.5 mm. The critical magnetic field is 42.75×103 A/m.
Given
r = 0.5 × 10-3 m, Hc = 42.75 × 103 A/m, Ic = ?
Solution:-
Ic = 2πr Hc
= 2×3.14×0.5×10-3 × 42.75 × 103
Ic = 134.25 Ampere
8. Calculate the critical current for a superconducting wire of lead having a diameter of 1 mm at 4.2K. Critical temperature for lead is 7.18 K and Hc(0) = 6.5 × 104 A/m.
Given
r = 0.5 × 10-3 m, T = 4.2 K, Tc = 7.18 K, H0 = 6.5 × 104 A/m, Ic = ?, Hc = ?
Solution:-

9. A voltage of 5.9×10−6 V is applied across a Josephson junction. What is the frequency of the radiation emitted by the junction?
Given
V = 5.9 × 10-6 V, v=?
Solution:-
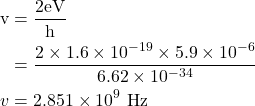
10. Prove that susceptibility of superconductor is -1 and relative permeability is zero.
Solution:-
eqn. 1
We know, the induced magnetic field B = μo (I+H)
In superconductor, B = 0.
Therefore eqn. (1) can be written as
0 = μo (I+H) eqn. 2
Since, μo #0,
I = -H
We know I/H = χ = -1 eqn. 3
Also, χ = μr = -1 eqn. 4
Equating eqn. (3) and (4) we get
μr -1 = -1
μr = 1 -1
μr = 0
Substituting eqn. (5) in (4) we get
Susceptibility χ= −1 and relative permeability μr = 0
| Read More Topics |
| Semiconducting materials – solved problems |
| Conducting materials – solved problems |
| Dielectric materials – solved problems |





