There are three ways of scanning the specimen by the ultrasonic transducer to get detailed image of the defect. The ultrasonic signals are transferred into the CRT screen to obtain the image of the defects.
The three important modes of ultrasonic display system are
- A-scan or Amplitude mode
- B-scan or Brightness mode
- C- scan or Time-Motion mode
A-scan or amplifude mode display
- A – scan is the simplest form of display.
- It gives only a one-dimensional image of the object.
- The transmitted and reflected echoes are displayed as vertical spikes.
- Similarly, the length of the vertical displacement is a measurement of the echo amplitude.
- The location of the reflected echo provides the location of defect.
- In this method, the transducer is fixed at one position.
- The ultrasonic flaw detection uses the A scan display.
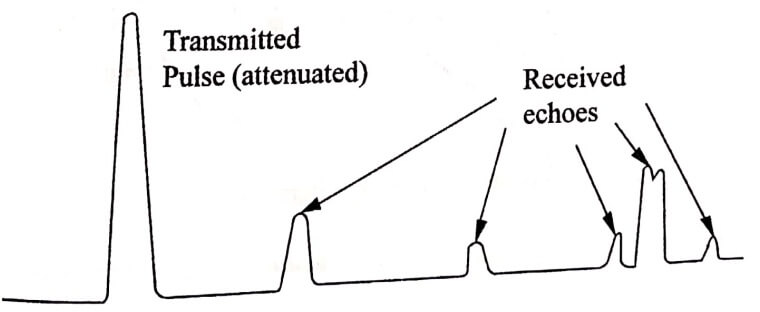
Fig. 1.1 Ultrasonic display principles
B – scan or brightness mode display
- In B-scan display, the brightness is related to the echo amplitude.
- It gives two dimensional view.
- The reflected echoes are displayed as dots.
- Every reflection produces a single dot as shown in (Fig.1.2).
- Intensity of the reflected echo signals indicates the brightness of the dot.
- The B-scan shows the reflection of the wave from the front and back surface of the test material and any flaws that lie between these two surfaces.
- In this method, the transducer is moved.
- The widespread applications of B-scan ultrasound in diagnostics are, namely to detect pregnancy, multiple foetuses and the age of the foetus.
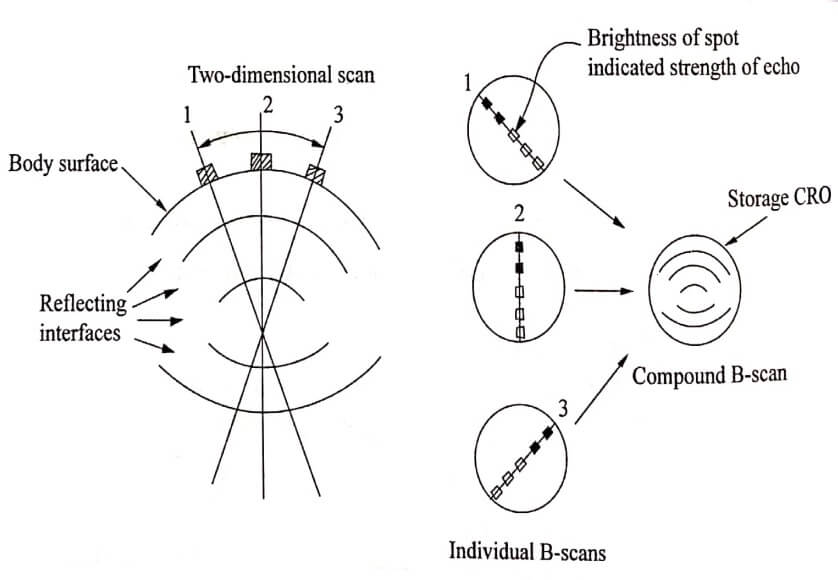
Fig. 1.2 B-scan display
C-scan or M-scan (Time-Motion mode)
- This can be used to display the size and positions of the specimen.
- In this mode the transducer is fixed so that the movement of the dots corresponds to the movement of the body.
- If the target moves during the scan, the pattern of movement is recorded with respect to the reflected echo.
- This produces line shading in the screen.
- The scan output with shades area indicates that the material have no defects.
- The scan output without any shades indicated the flaw’s shape.
- This mode is used in echocardiography.

Transmitted Pulse

Echo from moving target
Echo from stationary target
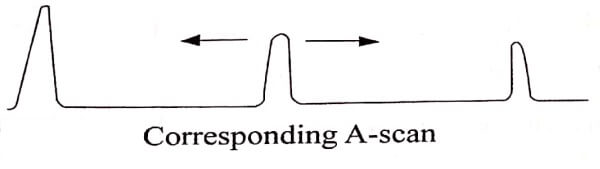
Fig. 1.3 M-scan of moving and stationary target with corresponding A-scan display
| Read More Topics |
| Non – Destructive Testing (NDT) |
| Photonics introduction and properties of laser |
| Ultrasonic testing methods |





