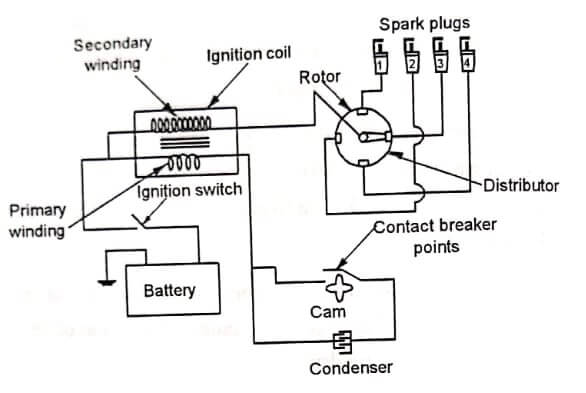
It is employed in petrol engines. Fig shows the wiring diagram of a simple coil battery ignition system of a four cylinder engine. This system is used in automobiles.
Construction:
It consists of a battery, ignition coil, condenser, contact breaker, distributor and spark plugs. Generally, 6 or 12 volts battery is used. The ignition coil consists of two windings primary and secondary. The primary winding consists of thick wire with less number of turns. The primary winding is formed of 200-300 turns of thick wire of #20-gage to produce a resistance of about 1.5ohms.
The secondary winding located inside the primary winding consists of about 21,000 turns of thin enameled wire of #38-40 gage with sufficiently insulated to withstand high voltage. It is wound close to the core with one end connected to the secondary terminal and the other end grounded either to the metal case or the primary coil. The condenser is connected across the contact breaker.
It prevents excess arcing and pitting of contact breaker points. The contact breaker is housed in the distributor itself. It makes and breaks the primary ignition circuit. The distributor distributes the high voltage to the respective spark plugs having regular intervals in the sequence of firing order of the engine.
(The sequence in which the firing or power occurs in a multi cylinder engine is known as firing order. The firing order of a 4-cylinder in-line engine is 1-3-4-2 or 1-4-3-2. The firing order of a 6-cylinder in-line engine is 1-5-3-6-2-4).
The spark plug is fitted on the combustion chamber of the engine. It produces spark to ignite the fuel-air mixture. The rotor of the distributor and contact breaker cam are driven by the engine. There are two circuits in this system. One is the primary circuit. It consists of battery, primary coil of the ignition coil, condenser and contact breaker. The other circuit is the
secondary circuit. It consists of secondary coil, distributor and spark plugs.
Working:
The battery ignition system switch is switched on and the engine is cranked. The cranking of the engine opens and closes the contact breaker points through a cam.
When the contact breaker points are closed:
- The current flows from the battery to the contact breaker points through the switch and primary winding and then returns to battery through the earth.
- This current builds up a magnetic field in the primary winding of the ignition coil.
- When the primary current is at the highest peak, the contact breaker points will be opened by the cam.
When the contact breaker points are opened:
- The magnetic field set up in the primary winding is suddenly collapsed.
- A high voltage (15000 volts) is generated in the secondary winding of the ignition coil.
- This high voltage is directed to the rotor of the distributor.
- The rotor directs this high voltage to the individual spark plugs in the sequence of the firing order of the engine.
- This high voltage tries to cross the spark plug gap (0.45 to 0.6mm) and the spark is produced. This spark ignites the fuel-air mixture.
Advantages:
- It provides better sparks at low speeds of the engine during starting and idling due to availability of maximum current throughout the engine speed range.
- The initial cost is low as compared with magneto ignition system.
- The maintenance cost is negligible except battery.
- Spark efficiency remains unaffected by various positions of the timing control mechanism.
Disadvantages:
- Frequent battery down occurs when the engine is not in use continuously. This causes starting trouble.
- The weight is greater than magneto ignition system.
- Wiring mechanism is more complicated.