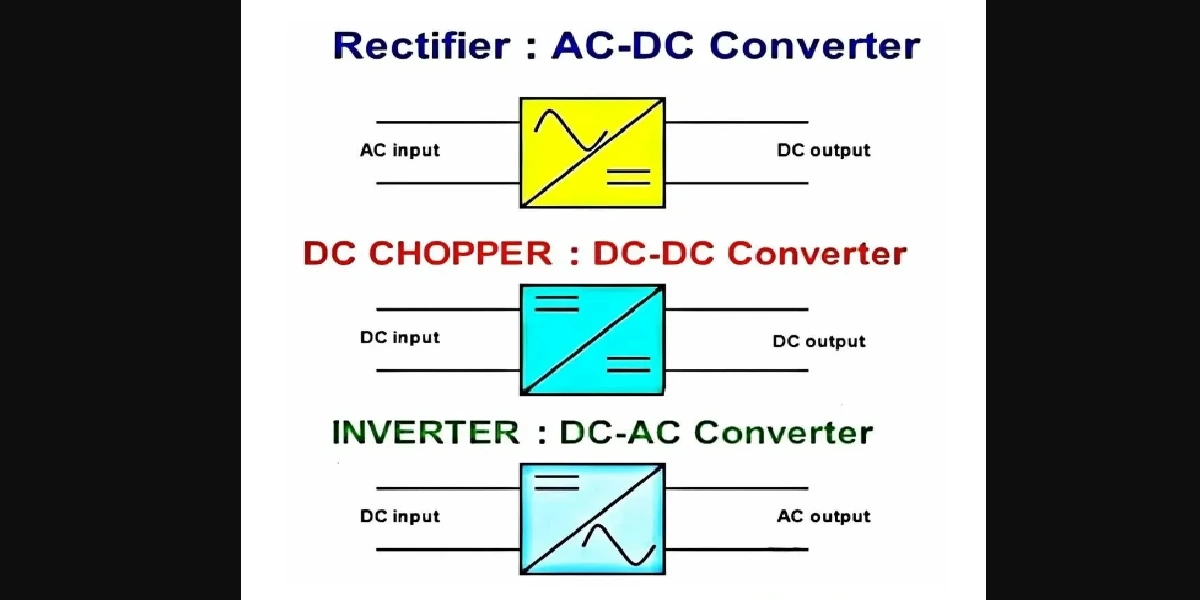
Did you ever think about how your laptop charger converts AC from the wall to DC for your machine? Or how solar panels supply power to your home? The magic lies in three magical building blocks: rectifiers, choppers, and inverters. These are the pillars of power electronics — the quiet achievers behind our hummin’ tech age.
In this guide for beginners, we will look at what these elements are, how they are used, and where you find them in daily life.
Understanding the Fundamentals
What is Power Electronics?
Power electronics is the study that is concerned with the conversion of electrical power from one form to another. Power electronics is a convergence of power engineering, electronics, and control systems to manage high voltages and currents effectively.
Why Learn about Rectifiers, Choppers, and Inverters?
Because they are ubiquitous. From mobile chargers to industrial drives, renewable energy systems, and electric cars — knowing them is your key to conquering contemporary power systems.
What Are Rectifiers?
Definition and Function
A rectifier is a piece of equipment that changes alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). It’s a one-way valve for electricity.
Types of Rectifiers
Half-Wave Rectifier
Permits only half of the AC waveform to pass through. Simple but wasteful.
Full-Wave Rectifier
Uses both halves of the AC signal. Needs a center-tapped transformer.
Bridge Rectifier
No need for center tap. Four diodes are employed to convert the whole AC signal to DC.
Applications of Rectifiers
Mobile phone chargers
DC motors
Welding gear
Power supplies in electronics
All About Choppers
What is a Chopper in Power Electronics?
A chopper is a DC-DC converter. It converts a constant DC input into a variable DC output. Imagine it as a dimmer for DC power.
Types of Choppers
Step-Up Chopper
Boosts the output voltage above the input.
Step-Down Chopper
Converts the output voltage below the input.
Two-Quadrant and Four-Quadrant Choppers
Regulate direction and polarity — applied in motor control and regenerative braking.
Applications of Choppers
Electric vehicles
Battery management systems
DC motor speed control
Solar energy systems
Introduction to Inverters
What is an Inverter?
An inverter does the reverse of a rectifier. It transforms DC to AC — what the majority of home appliances need.
Types of Inverters
Square Wave Inverter
Cheap and simple, yet not ideal for sensitive equipment.
Sine Wave Inverter
Emulates the utility grid — ideal for household use.
Modified Sine Wave Inverter
A middle ground between the two — good enough for general use.
Applications of Inverters
UPS systems
Solar power systems
Electric vehicle powertrains
Portable power stations
Real-Life Examples and Use Cases
In Home Appliances
Chargers (Rectifiers)
Voltage Regulators (Choppers)
Solar Inverters (Inverters)
In Industry
DC Drives use choppers
Power rectification for control panels
Inverter drives for motors
In Renewable Energy Systems
Solar panels produce DC – inverters convert it to AC
Battery storage systems depend on rectifiers and choppers
Latest Trends in Power Electronics
Smart Inverters
AI-controlled inverters that optimize grid interaction.
High-Efficiency Choppers
For fast charging electric vehicles.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) in Rectifiers
Enables smaller, faster, and more efficient components.
Conclusion: Power electronics is not about circuits and components alone — it’s the secret language of modern technology. If you want to venture into solar energy, electric vehicles, or smart grids, a clear grasp of rectifiers, choppers, and inverters provides a solid foundation.
Read also: DC Motors Definition Working Types Uses