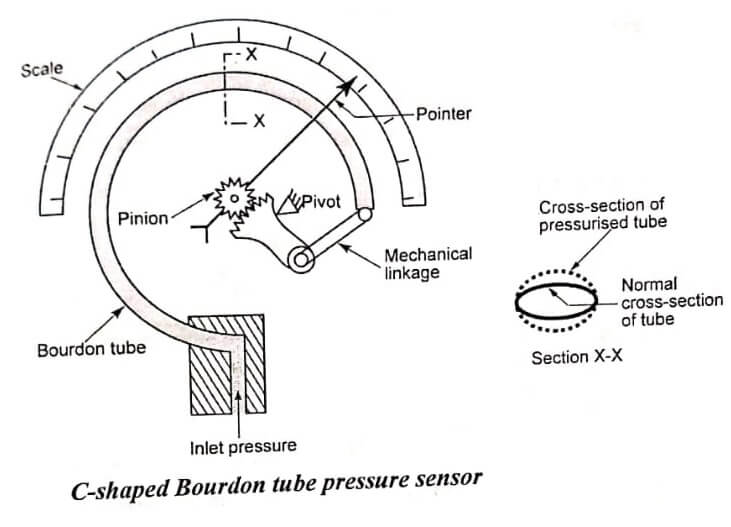
The bourdon tube pressure sensor instrument is one of the oldest pressure sensing instruments in use today. It is widely used in applications where inexpensive static pressure measurements are needed. The bourdon tube consists of a thin-walled C-shaped tube that is flattened diametrically on opposite sides to produce a cross-sectional area elliptical in shape, having two long flat sides and two short round sides. The tube is bent lengthwise into an arc of a circle of 270 to 300 degrees. Bourdon tube pressure sensor is open to external pressure input on one end and is coupled mechanically to an indicating needle on the other end, as shown schematically in fig.
Pressure applied to the inside of the tube causes distention of the flat sections and tends to restore its original round cross-section. This change in cross-section causes the tube to straighten slightly. Since the tube is permanently fastened at one end, the tip of the tube traces a curve that is the result of the change in angular position with respect to the center. Within limits, the movement of the tip of the tube can then be used to position a pointer or to develop an equivalent electrical signal to indicate the value of the applied internal pressure.
The deflection of the Bourdon tube can be measured in any number of ways. For example, it can be detected via a mechanically-coupled indicating needle [refer fig], a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) as described in the diaphragm pressure gauge [refer fig (b)], a potentiometer [refer fig(b)], or with many other displacement sensors.
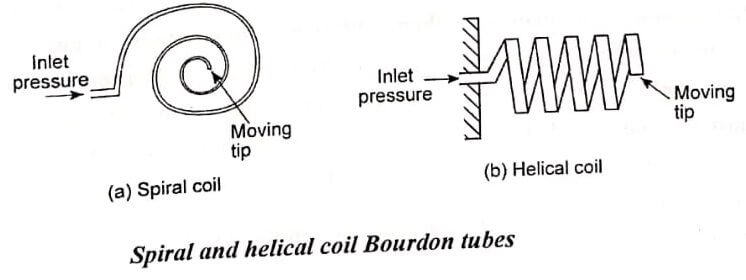
To increase their sensitivity, Bourdon tube elements can be extended into spirals or helical coils [fig (a) and (b)]. This increases their effective angular length and therefore increases the movement at their tip, which in turn increases the resolution of the transducer.
Advantages:
- Portable
- Convenient to use
- No leveling required
Disadvantages:
- Limited to static or quasi-static measurements.
- Accuracy may be insufficient for many applications. A mercury barometer can be used to calibrate and check Bourdon Tubes.
- See More : Bellows pressure gauge
- See More : Laser interferometer
- See More : Metric system of measurement
- See More : Radio over fiber links