1. Hysteresis
Hysteresis of a SMA is defined as the difference between the temperature at which the material is 50% transformed to austenite when heating and 50% transformed to martensite when cooling.
When the temperature is decreased in a metallic material, the phase transformation takes place from austensite to martensite. This transformation takes place not only at a single temperature, but over a range of temperatures.
The hysteresis curve for a shape memory alloy is shown below.
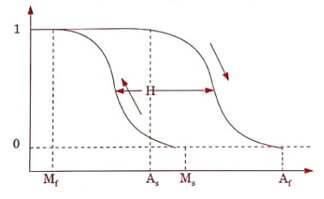
Figure 1.1 Transformations Vs Temperature
2. Pseudo elasticity
When a metallic material is cooled from a temperature to a lower temperature T1 , it deforms and changes its shape. On reheating the material to Temperature T2 , the shape change is recovered so that the material returns to its original state. This effect is known as pseudo elasticity or thermo elastic property.
3. Super elasticity
Super elasticity is a property of SMA. When a material is deformed at a temperature slightly greater than its transformation temperature super elasticity property appears [Rubber like property].
Properties of Ni – Ti alloy
Ni – Ti is a compound of Nickel and titanium and it finds many applications in the field of engineering due to the following properties.
- It has greater shape memory strain.
- It has more thermal stability and excellent corrosion resistance.
- It has higher ductility and more stable transformation temperatures.
- It has better bio-compatibility and it can be electrically heated.
Physical and Mechanical Properties of Ni – Ti alloy
| Properties | Value |
| Melting temperature | 1573K |
| Density | 6.45 x 10-3 Kg/m3 |
| Resistivity at Austenite | 100μΩ |
| Resistivity at Martensite | 70μΩ |
| Thermal conductivity at Austenite | 18 Wm-1K-1 |
| Thermal conductivity at Martensite | 8.5 Wm-1K-1 |
| Young’s modulus at Austenite | 83 Gpa |
| Young’s modulus at Martensite | 28 – 41 Gpa |
| Yield Strength at Austenite | 195 – 690 Mpa |
| Yield Strength at Martensite | 70 – 140 Mpa |
| Ultimate tensile strength | 895 Mpa |
| Transformation temperature | 73 – 383 K |
| Shape memory strain | 8.5 % maximum |
- SMAs are Simple, compact and safety.
- SMAs have Good biocompatibility.
- SMAs are Strong and have high corrosion resistance.
- They have High power to weight ratio.
- SMAs have Poor fatigue.
- They are Expensive.
- SMAs have Low energy efficiency.
- SMAs have Complex control.
- They have Limited bandwidth.
- It is used as a thermostat valve in cooling system.
- It is used as a sealing plug for high pressure.
- It is used as a fire safety valve.
- It is used for cryofit hydraulic pipe couplings.
- It is used for eye glass frame, toys, liquid safety valve.
- It is used to make microsurgical instruments, orthopedic implants.
- It is used as blood clot filter and for fracture pulling.
- It is used to make antenna wires in cell phones.
- It can be used as circuit edge connector.
| Read More Topics |
| Hard and soft magnetic material |
| Charge densities in a semiconductor |
| Electrical conductivity in intrinsic semiconductor |





