- It is a method in which the reaction or thermal decomposition of gas phase species at higher temperature (500 – 1000°C) and then nanoparticles deposition on a substrate takes place.
- In chemical vapour deposition method carbon nanotubes are also grown from the decomposition of hydrocarbons at temperature range of 500 to 1200°C.
- In this process, the substrate is placed inside a reactor to which a number of gases are supplied. The fundamental principle of the process is that a chemical reaction takes place between the source gases. The product of that reaction is a solid material with condenses on all surfaces inside the reactor.
Example of CVD technique
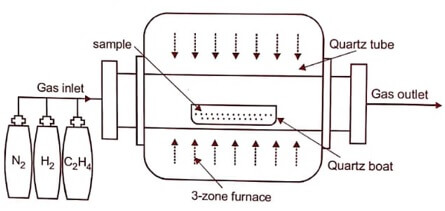
Fig 1.1
- Aerosol spray pyrolysis (Pyrolysis is the chemical decomposition of organic materials by heating in the absence of oxygen or any other reagents is th example of CVD technique.
- In which high aqueous metal salts are sprayed in the form of fine mist and then passed into a hot flow tube.
- In the hot flow tube pyrolysis converts the salts into the final products on the substrate.
- In this method the materials are mixed in a solution, homogeneous mixing is obtained at the atomic level.
- The pyrolysis at low temperature gives the particles in the size range 5 – 500 nm .
- In this CVD method catalysts are used for better chemical reactions.
- When the catalyst is in nanosize, dispersion of particles is happened due to templating effect.
- In the Production of carbon nanotubes using the decomposition of ethene with hydrogen, Fe, Co or Ni based catalysts are used.
- the size and distribution of the catalyst particles determine the internal diameter of the nanotube.
| Read More Topics |
| Semiconducting material – Questions and Answers |
| Electrical conductivity in intrinsic semiconductor |
| Mobility and conductivity in semiconductors |





