Based on the crystal structure point of view, the solids can be classified into two categories namely:
- Crystalline (or) Crystals and
- Non-crystalline (or) Amorphous solids.
Crystalline solids or Crystals
Crystalline solids (or) crystals are those in which atoms (or) molecules are arranged in some systematic (or) regular pattern.
In these materials, the arrangement of atoms takes a periodically repeating pattern throughout the body of the crystal. Therefore, crystalline solids have well defined geometrical form i.e., they have defined faces and angles between them.
Further when a crystal breaks, all the broken pieces will have a regular shape. The crystalline solids have directional properties and therefore they are called anisotropic substances.
Examples : Aluminium, Copper, Gold, Silver etc.
A crystalline solid will be in two forms, namely:
- Single crystal and
- Poly crystal.
In a single crystal, the entire solid consists of only one crystal. These single crystals are produced artificially from their vapour (or) liquid state.
In a poly-crystalline material, an aggregate of many small crystals are separated by well-defined boundaries. These crystals will have a sharp melting point.
Properties of crystalline solids
- They have definite external geometrical shape.
- Crystalline substances are anisotropic i.e. the physical properties like thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity etc, have different values in different directions.
- They have uniform chemical composition as the bonds between all the ions, atoms or molecules are of equal strength.
- The crystalline material has a fixed melting point.
Non-Crystalline or Amorphous solids
Non-crystalline (or) amorphous solids are those in which the atoms (or) molecules are not arranged in a regular pattern.
In other way we can say that in amorphous solids the same atomic groups are arranged randomly in all directions. Therefore, non-crystalline solids don’t have well defined geometrical form.
These solids have no directional properties and therefore they are called isotropic substances. These amorphous solids do not have a sharp melting point.
Examples : Glass, Plastic and Rubber etc.
Properties of non-crystalline soilds
- They have no definite external geometrical shape.
- They are isotropic i.e. they have same physical properties in all direction.
- They do not possess uniform chemical composition. Thus, bounds between all the atoms and molecules are not of equal strength.
- They do not have a fixed melting point due to unequal strength between all the atoms.
Single crystal, poly crystalline solids and amorphous solid are illustrated in fig.
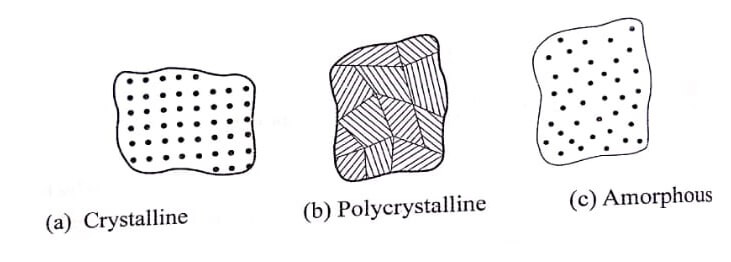
Differences between crystalline and amorphous solids
| S.No | Crystalline solids | Amorphous solids |
| 1. | Regular arrangement of atoms gives defnite and geometric shape. | Random arrangement of atoms does not give definite and geometrical shape. |
| 2. | They are anisotropic. | They are isotropic. |
| 3. | They have sharp melting point. | They do not have sharp melting point. |
| 4. | They possess internal symmetry. | They do not possess internal symmetry. |
| 5. | Examples: Diamond, NaCl, KCl, Copper, etc. | Examples: Glass, Plastic, Rubber etc. |
| Read More Topics |
| Dielectric materials questions and answers |
| Classification of nonlinear materials |
| Semiconducting materials solved problems |





