Based on the area of the hysteresis loop, the magnetic materials are classified into soft and hard magnetic materials.
Generally the magnetic materials are classified into two types.
They are
- Soft Magnetic materials
-
Hard Magnetic materials
Soft Magnetic materials
These are materials which are easily magnetized and demagnetised. They are also called as temporary magnets.
Magnetic materials which do not retain the alignment of magnetic domains after the removal of the external magnetic field are known as soft magnetic materials.
Examples: Pure iron, Cast iron, Carbon steel, Silicon steel, manganese and nickel steel, soft ferrites.
Hard Magnetic materials
These are materials which are easily magnetised but are difficult to demagnetize. They are called as permanent magnets.
Materials which retain permanently the alignment of the magnetic domains even after the removal of the external magnetic field are known as hard magnetic materials.
Examples: Tungsten steel, Cobalt steel, Hypernic (contains 50% nickel and 50% iron).
Difference between Soft & Hard Magnetic materials
| Sl.No. | Soft Magnetic materials (Temporary magnet) | Hard Magnetic materials (Permanent magnet) |
| 1. | Magnetic materials which can be magnetized and demagnetised. | Magnetic materials which can be easy magnetized and difficult to demagnetize. |
| 2. | They have high permeability and Susceptibility. | They have low permeability and Susceptibility. |
| 3. | Magnetic energy stored is not high. | Magnetic energy stored is high. |
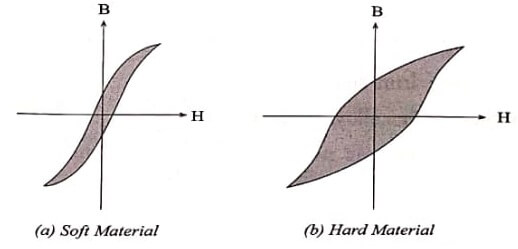
| 4. | Hysteresis loop is very narrow. | Hysteresis loop is very broad. |
 |
||
| 5. | Low hysteresis losses due to small hysteresis loop area | Large hysteresis losses due to large hysteresis loop area. |
| 6. | Coercivity and retentivity are small. | Coercivity and retentivity are large. |
| 7. | The eddy current loss is small due to its higher resistivity. | The eddy current loss is more due to its smaller resistivity. |
| 8. | Movement of domain wall is easy and hence even for a small applied field large magnetization occurs. | Movement of domain wall is not easy due to the presence of impurities and hence large field is required. |
| 9. | These materials are free from irregularities like strain or impurities. | These materials have large amount of impurities and lattice defects. |
| 10. | These are produced by heating them into sufficient temperature & then allowed to cool slowly connecting process. | This are produced by heating them into sufficient temperature & them plunging it suddenly into cold oil. |
| 11. | Examples: Iron silicon alloy, Nickel iron alloy, silicon steels, ferrites. | Examples: Tungsten steel, Cobalt steel. Alini, Alnico, Cunife. |
| 12. | Applications : They are used in electric motor, generator, transformers, relays, telephone receivers, radar and Sonar equipments. | Applications : They are used in loud speakers and electrical measuring instruments. |
| Read More Topics |
| Classification of magnetic materials |
| Definition and properties for diamagnetism |
| Domain theory of ferromagnetism |





