The differences between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system according to their origin, character and effect on respective organs are listed in table.
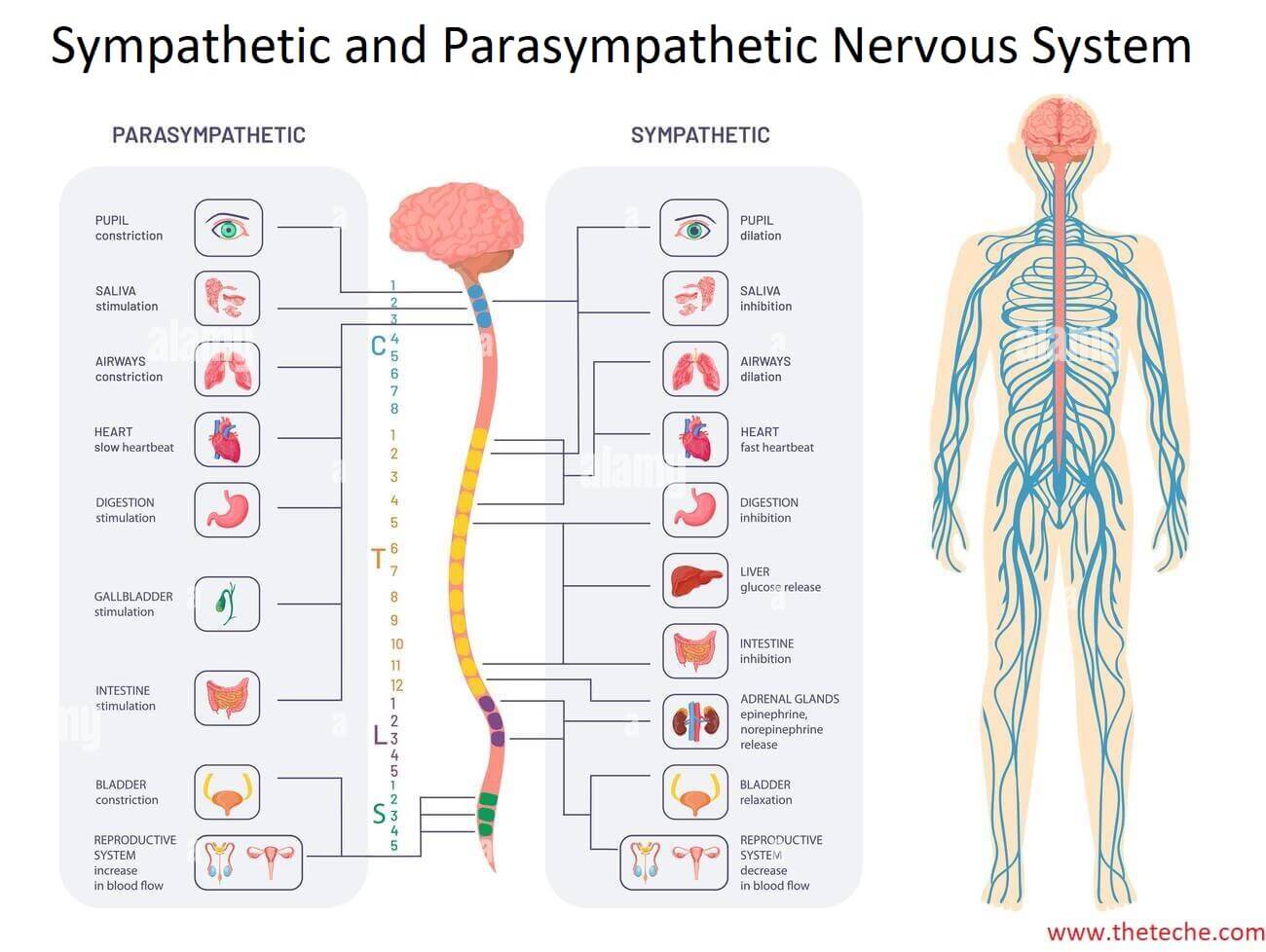
| Sympathetic | Parasympathetic | |
| Origin | From all thoracic and upper 3 lumbar segments. | From cranial 3, 7, 9, 10 and sacral 2, 3, 4 segments. |
| Character | Short preganglionic and long post-ganglionic fibres. | Long preganglionic and short post-ganglionic (terminal ganglia). |
| Effect on Organs
Heart 1. H.R 2. Atrioventricular conduction 3. Atrial Refractory period 4. Atrial conduction 5. Ventricular conduction and contraction |
1. Tachycardia 2. Increase 3. Decrease 4. Increase 5. Increase |
1. Bradycardia 2. Decrease 3. Decrease 4. Increase 5. No effect |
| Smooth Muscles
1. Eye 2. Bronchi 3. GIT 4. Urinary bladder 5. Blood vessels |
1. Mydriasis 2. Bronchodilatation (relaxation) 3. Relax wall and contact sphincters 4. Urine retention 5. Vasoconstriction and dilatation |
1. Miosis and contraction of ciliary muscle 2. Bronchospasm (contraction) 3. Contract wall and relax sphincters 4. Micturition 5. Vasodilatation of some vessels |
| Secretions
1. Salivary 2. Sweat |
1. Thick viscid 2. Increase |
1. Profuse watery 2. No effect |
| Sex Organs | Ejaculation | Erection |
| Read More Topics |
| Transmembrane enzyme linked receptors |
| G Protein coupled receptors |
| Factors affecting drug receptor interaction |
| Plasma protein binding of drug |