Expression for electrical conductivity in intrinsic semiconductor
The general expression for the electrical conductivity, σ = neμ
The intrinsic electrical conductivity, σi = [neμe + peμh]
But n = p = ni
Therefore σi = [nieμe + nieμh]
σi = nie [μe + μh]
where, μe electron mobility and μh hole mobility
![]()
The electrical conductivity depends on the negative exponential of and the mobilities μe and μh . But the [μe + μh] is found to be proportional to T -3/2 . So that we can neglect [μe + μh] .
The Electrical conductivity
eqn(1)
![]()
where, C is a constant.
Taking log on both sides of equation (1),
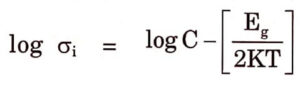
![]()
Fig (1)
From the graph, we know that the electrical conductivity increases when temperature increases.
| Read More Topics |
| Mobility and conductivity in semiconductors |
| Elemental and compound semiconductor |
| Types of semiconductors |





