1.Define nuclear fission. Give an example.
Ans: Nuclear fission is the process of splitting of a heavy nucleus into two lighter nuclei of nearly comparable masses with release of energy.
Example: Fission of U-235 by neutrons.
2. Mention few important characteristics of nuclear fission.
Ans: (i) Upon capturing a neutron, a heavy nucleus splits into two or more nuclei.
(ii) Two or more neutrons are produced by fission of each nucleus.
(iii) Enormous amount of energy is produced as a result of conversion of small mass into energy.
(iv) All the fission products are radioactive giving off beta and gamma radiations.
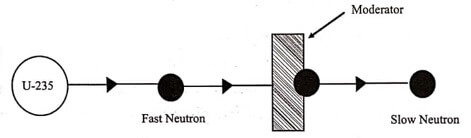
3. How a nuclear fission becomes a chain reaction?
Ans: When the number of secondary neutrons available in each fission reaction (multiplication factor) is controlled to one, the fission reaction becomes a chain reaction.
4. State critical mass.
Ans: Critical mass of a fissionable material is the minimum mass of fissionable material required to sustain a chain reaction. The critical mass varies for each reaction. For U-235 fission reaction it is about 10kg.
5. What is sub-critical mass and super-critical mass of U235?
Super-critical mass is a mass greater than its critical mass. In this case, the secondary neutrons emitted increases and hence the rate of fission chain reaction also increases rapidly which leads to explosion as in atom bomb.
6. What are the uses of nuclear energy ?
(i) generating electricity
(ii) the treatment of diseases like cancer
(iii) the improvement of agriculture and industry.
7. What is nuclear energy or fission energy?
Ans: The fission of U235 nucleus by slow neutrons released enormous amount of energy. The fission of U235 is an exo-ergic reaction. The energy released is called nuclear energy or fission energy.