Fibre optical communication system is the transmission of information by propagation of optical signal through optical fibres over a required distance.
This involves encoding of electrical signal (audio or video signal) to optical signal at the transmitting end and conversion of optical signal back to electrical signal at the receiving end.
The fibre optical communication system consists of three important parts as shown in fib 1.1
- Transmitter,
- Optical fibre,
- Receiver
(a) Information signal source
The information signal source may be voice, music, video signals etc, which is in the analog form to be transmitted, is converted from analog signal to electrical signal.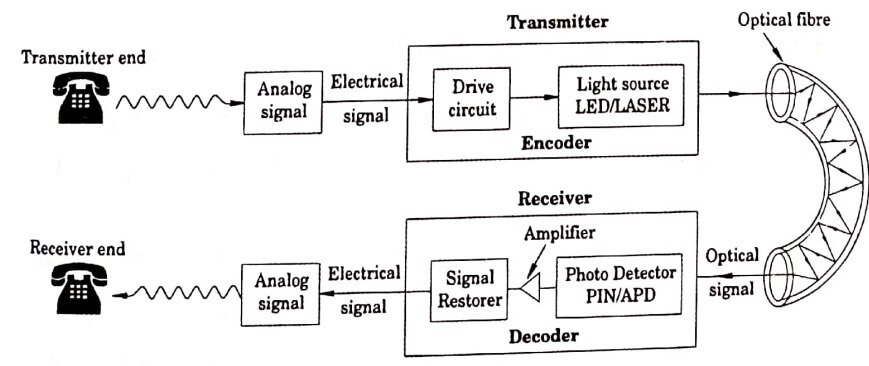
Fig 1.1 Fibre optical communication system
(b) Transmitter
The transmitter consists of a drive circuit and a light source. The drive circuit converts the electric input signal into digital pulses and the light source converts that into optical pulses. The light source usually used is LED. Here the electric pulses modulate the intensity of light source (Laser (or) LED) and are focussed into the optical fibre.
(c) Optical fibre
It acts as a waveguide and transmits the optical pulses towards the receiver based on the principle of total internal reflection.
(d) Receiver
The photo detector is a receiver which receives the optical pulses and converts it into electrical pulses. Further the signals are amplified by an amplifier. These electrical signals are decoded (i.e.) converted from digital to analog signals. Thus, the original electrical signal is obtained in analog form, with the same information.
In this way information is transmitted from one end to other end through optical fibres.
| Read More Topics |
| Three types of optical fibre |
| Introduction and construction of fibre optics |
| Principle and propagation of light in optical fibres |





