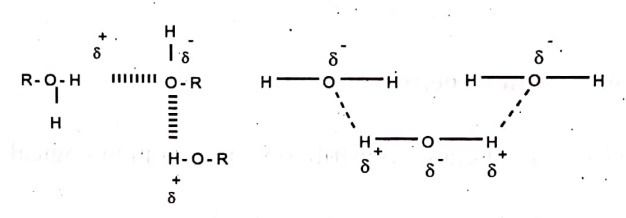
Hydrogen bonding is a type of dipole-dipole interaction between non-bonding electron pairs of hetero atoms like N, S, O and electron deficient hydrogen atom in polar bonds such as OH,NH,F etc., these are weak bonds (10kcal/mol.) and denoted as dotted lines. eg.

The compounds that are capable, of forming hydrogen bonding are only soluble in water. Proteins are held in specific configuration by hydrogen bonds and denaturation of protein involves the breaking up of the same bond. Generally hydrogen bonding is classified into two types.
- Intermolecular hydrogen bonding
- Intramolecular hydrogen bonding
i) Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding occurs between two or more molecules.
ii) Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding occurs within the molecules

Hydrogen Bonding and Biological Action
Hydrogen bonding is an important parameter in chemical process. It is responsible for water unique solvent capabilities. Hydrogen bonds hold the two strands of DNA helix together and in protein they hold α-helix and β-sheet together. It is responsible for the determination of three dimensional structure of folded protein including enzymes and antibodies.
Antibodies produced in the body binds to antigen through a series of interaction including hydrogen bonds. The presence or absence of hydrogen bond is very important in designing a drug. For example, (i) Antipyrine, 1- Phenyl – 2, 3 – dimethyl – 5 – pyrazolone has analgesic activity but 1Phenyl – 3 – methyl – 5 – pyrazolone is inactive. This is due the formation of hydrogen bonding in the 1 – Phenyl – 3 – methyl – 5 -pyrazolone, gives rise to linear polymer which cannot pass through membrane.

(ii) Salicylic acid (o – Hydroxy benzoic acid) has antibacterial activity but not the p-isomer and m-isomers ie. p and m – Hydroxy benzoic acids are inactive. This is because, salicylic acid forms intra molecular hydrogen bonding, so it is less water-soluble and its partition coefficient is also greater. The m and the p isomer can form intermolecular H-bonds, results in dimer and does not easily pass through the bio membranes. The partition co-efficient of it is also less and hence low antibacterial action.