Let us discuss some of the important parameters which are used to describe the crystal structure.
Number of atoms per unit cell
The total number of atoms present in an unit cell is known as number of atoms per unit cell.
The distribution of atoms is different in lattice structure. This can be determined if the arrangement of atoms inside the unite cell is known.
Coordination number
Each atom in a crystalline structure is surrounded by other atoms.
It is the number of nearest neighbouring atoms coordinate or contact with a particular atom in a given structure is called coordination number.
If the coordination number is high, then the structure will be more closely packed. It signifies the tightness of packing of atoms in the crystal.
Atomic radius
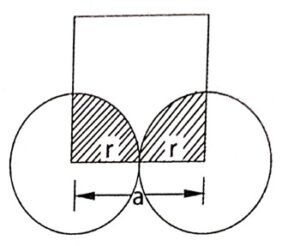
Atomic radius is defined as half of the distance between the centre of two neighbouring atoms.
It is denoted by the symbol ‘r’. It is usually expressed in terms of cube edge ‘a’. (Lattice parameter).
2r = a
![]()
Atomic packing factor (or) Packing density
Atomic packing factor is defined as the ratio between the volume occupied by the total number of atoms per unit cell (v) to the total volume of the unit cell (V).
Volume occupied by the total
![]()
![]()
Cubic crystal structure
The simple form of seven crystal systems is cubic crystal system. There are three types of cubic crystals.
They are –
- Simple Cubic (SC) Crystal
- Body – Centered Cubic (BCC) Crystal
- Face – Centered Cubic (FCC) Crystal
| Read More Topics |
| Classification of solids – crystal physics |
| Classification of nonlinear materials |
| Conducting materials – solved problems |





