The Internal Combustion engines (I.C engine) is a heat engine that converts chemical energy of fuel into mechanical energy. Chemical energy of a fuel is first converted into thermal energy by means of combustion or oxidation with air inside the engine. This thermal energy is again converted into useful work through mechanical mechanism of the engine. Most of the internal combustion engines are reciprocating engines having pistons that reciprocate back and forth in cylinders internally within the engine. This chapter mainly concentrates on the study of this type of engine.
Internal Combustion Engines Construction
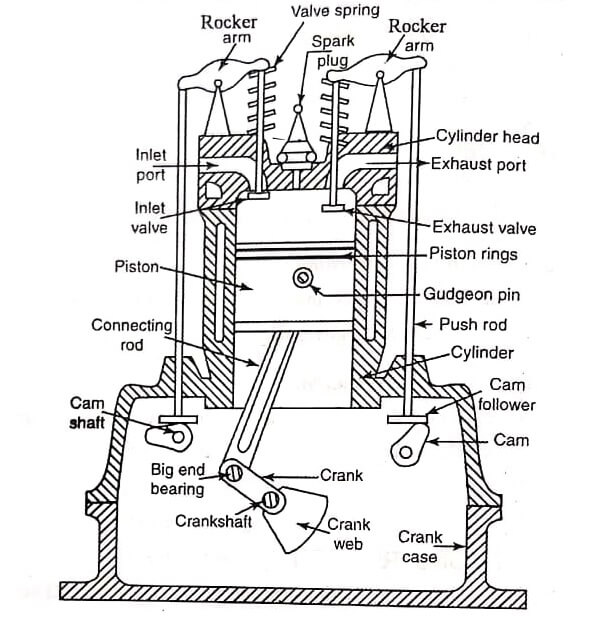
Fig shows the construction details of an I.C engine (Four stroke petrol engines). The main components of a four stroke cycle engine are cylinder, piston, connecting rod, piston rings, cam shaft, crank shaft, crank case, inlet and outlet valves, spark plug, cylinder head, push rod, gudgeon or piston pin, rocker arm, cam follower, valve spring, big end bearing, inlet port etc. The piston reciprocates inside the cylinder. Piston rings are inserted in the circumferential grooves of the piston. The cylinder and cylinder head are bolted together.
The reciprocating motion of the piston is converted into rotary motion of the crankshaft by means of a connecting rod and crank. The small end of the connecting rod is connected to the piston by a gudgeon pin or piston pin. The big end of the connecting rod is connected to the crank pin. Crank pin is bearing surface and it is rigidly fixed to the crankshaft.
The crankshaft is mounted on the main bearing. The main bearings are housed in the crankcase. Camshaft is driven by the crankshaft through timing gears. The camshaft actuates the inlet and outlet valves. The valve springs are provided to bring back the valves in the closed position.
The oil sump containing lubricating oil is provided at the bottom of the crankcase. Lubricating oil is circulated to the various parts of the engine from the oil sump. A spark plug is provided in petrol engines to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the engine cylinder. An injector is provided in diesel engines to inject the fuel into hot compressed air during power stroke.
IC Engines Components and its Functions
Major components found in most of the reciprocating internal combustion engines are explained below:
Cylinder block : It is the main body of an engine which contains cylinders. The piston reciprocates inside the cylinder to develop power. The cylinders are accurately finished to accommodate pistons. The cylinder block also houses crank, crankshaft, piston and other engine parts. During combustion, high pressure and temperature will be developed inside the cylinder. Therefore, it should be made of material which can resist high temperature and pressure.
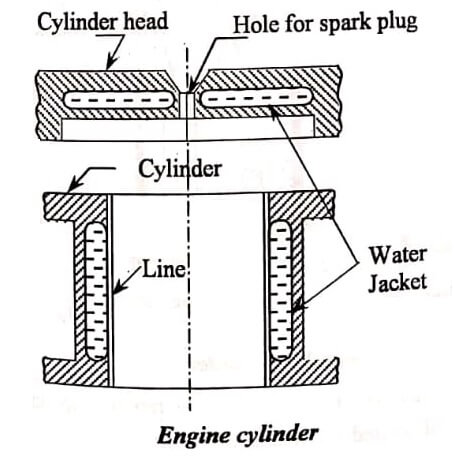
It is made of grey cast iron or aluminum with steel sleeves. In water- cooled engines, the cylinder block is provided with water jackets for circulation of cooling water as shown in fig.
Cylinder head : The cylinder head is bolted to the top of the cylinder block. It houses the inlet and exhaust valves through which the charge is taken inside of the cylinder and burnt the gases arc exhausted to the atmosphere from cylinder. It also contains spark plug hole or injector hole and cooling water jacket, The materials used for cylinder heads are cast iron, aluminum alloy etc.
Crank case : It may be cast integral with the cylinder block. Sometimes, it is made of cast separately and bolted to the cylinder block. It supports the crankshaft and camshaft with the help of bearings. Sometimes, the bottom of crankcase may be used as oil sump. It is made of cast iron, aluminum alloys or alloy steels.
Oil sump or oil pan : Oil sump is fitted at the bottom of crankcase by using gasket. It contains lubricating oil. A drain plug is provided to the oil sump to drain out the oil. It is made of pressed steel sheet.
Cylinder liners : Inside the cylinder, the piston constantly moving up and down which will cause wear of cylinder. When the cylinder diameter is increased beyond certain limit, we may have to discard the entire cylinder block which is costly. To avoid earlier cylinder wear, a separate liner which is in the form of sleeve is inserted into the cylinder bore. Here, the wear will take place in the liner only which can be replaced easily when worn out. There are two types of liners:
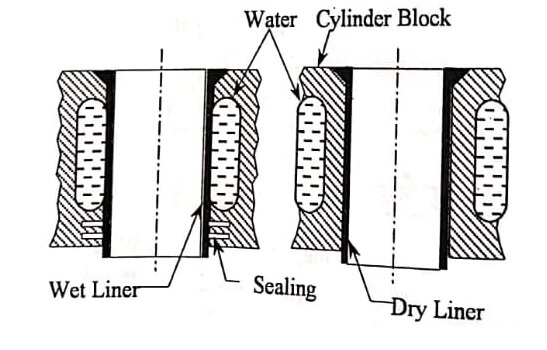
- Wet liner – The liners are surrounded by cooling water as shown in fig. It provides wear-resisting surface for the piston to reciprocate. It also acts as a seal for the water jacket.
- Dry liner – Dry liners have metal-to-metal contact with the cylinder block. They are not directly in touch with cooling water.
Liner material should withstand abrasive wear and corrosive wear. Chromium plated mild steel tubes are used as liners.
Piston : It is a cylindrical shaped mass that reciprocates inside the cylinder. The piston serves the following purposes:
- It acts as a movable gas tight seal to keep the gases inside the cylinder.
- It transmits the force of explosion in the cylinder to the crankshaft through connecting rod.
The top of the piston is called as crown and sides are called as skirt. It has grooves to hold piston rings and oil ring. It is opened at the bottom end and closed at the top. Sometimes, T-slots are provided in the skirt to allow expansion.
Piston is made of cast iron, Aluminum alloy, chrome-Nickel alloy, nickel-iron alloy and cast steel. They are manufactured by casting or forging method.
They are used to maintain air tight sealing between piston and cylinder to prevent gas leakages. Piston rings are fitted in the grooves which arc provided in the top portion of the piston skirt. Two types of piston rings are used in a piston.
- Compression rings : These rings provide an effective seal for the high pressure gases inside the cylinder. Each piston is provided at least with two compression rings.
- Oil rings : These rings wipe off the excess oil from the cylinder walls. It also returns this excess oil to the oil sump through the slots provided on the rings. The materials used for piston rings are cast iron, alloy cast iron containing silicon and manganese, alloy steels etc. Piston rings are generally coated with chromium or cadmium.
- Connecting rod : It is used to connect the piston and crankshaft with the help of bearing. It is usually steel forging of circular, rectangular, I, Tor H cross- section. Its small end is connected with the piston by the piston pin and its big end is connected to the crank by the crank pin.
| Read More Topics |
| What do you mean by cost quality? |
| Describe the various quality statements |
| Discuss the contribution of Juran for quality in detail |