Fibre optics is a branch of physics which deals with the transmission of light through a transparent glass or optical fibres. This is based on the principle of total internal reflection.
Here, light is used to transmit the information from one place to other. Instead of using an electrical signal travelling over a cable, the information is inserted on a light beam and transmitted through a cylinder of transparent dielectric medium, called optical fibre.
In 1870, John Tyndall gave the demonstration of this principle. Later in 1880, Alexander Graham Bell reported the transmission of speech using light beam.
Optical Fibre
An optical fibre is a very thin, flexible thread of transparent plastic or glass in which light is transmitted based on the principle of total internal reflections.
Construction of opticalfibre
It consists of three section : (i) the core (ii) the cladding and (iii) the jacket.
(i) Core : It is the innermost part and is made of glass or plastic.
(ii) Cladding : The core is surrounded by a layer of material (glass or plastic) having lower refractive index than the core. This layer is called cladding. It helps to keep the light within the core. The cladding is generally made of silicon or Teflon.
(iii) Jacket : The outer section which covers the cladding is known as jacket. The jacket is made of plastic or polymer. It protects the optical fibre from moisture, mechanical shock and other environmental hazards (viz. pollution and radiation etc.)
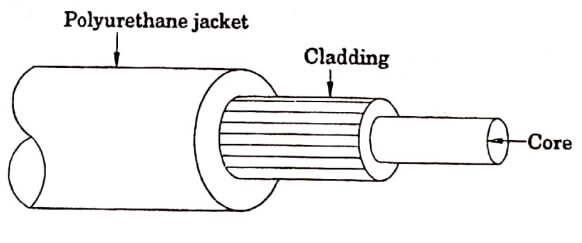
Fig 1.1 Structure of optical fibre
Dimension of Fibre
The diameter of the core is usually in the order of 5μm to about 50μm. The diameters of the cladding and the jacket are about 125μm and 200μm respectively.
Features of optical fibres
-
It is light in weight.
-
It is smaller in size and is flexible, so that it can bend to any position.
-
It is non-conductive, non-radiative and non-inductive.
-
It has high bandwidth and low loss.
-
There is no short circuiting.
-
There is no internal noise (or) cross talks.
-
It can withstand any range of temperatures and moisture conditions.
| Read More Topics |
| Fibre optical communication system |
| Types of semiconductor laser |
| Photonics introduction and properties of laser |





