Lead acid battery was invented by Gaston Plante in 1859. A lead acid storage cell is an electrochemical cell, which stores electric charge.
-
This acts as a voltaic cell and as an electrolytic cell.
-
On supplying electrical energy, this acts as a voltaic cell.
-
On recharging, the cell acts as an electrolytic cell.
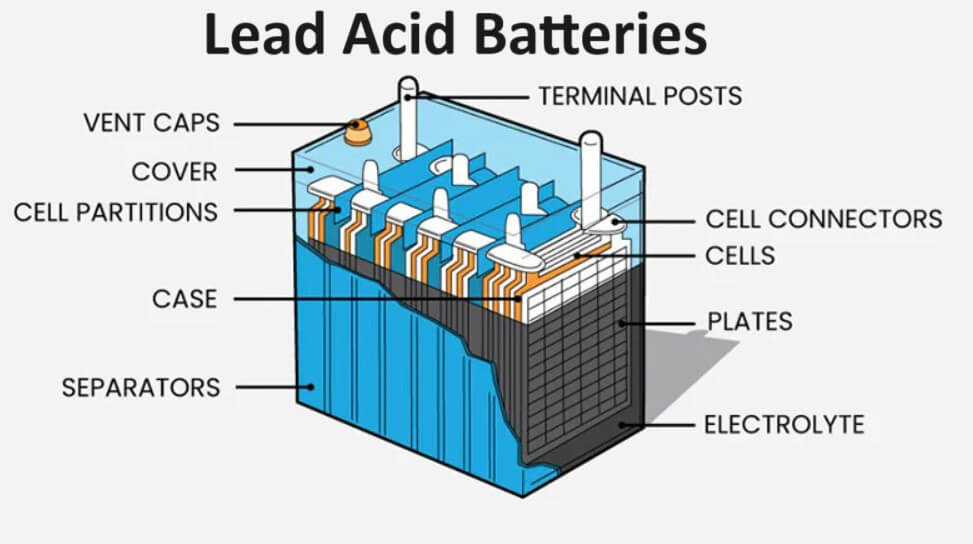
The cell consists of a polypropylene container containing six lead-acid electrochemical cells connected in series.
A lead acid battery consists of a negative electrode of lead as the anode and a positive electrode of lead dioxide (PbO2) as the cathode. A series of lead plates and PbO2 plates i.e., anode and cathode are placed in parallel. They are kept alternately and the plates are separated from one another by rubber or glass fibre. The entire electrode pairs are immersed in 20% sulphuric acid solution. (Fig. 1)
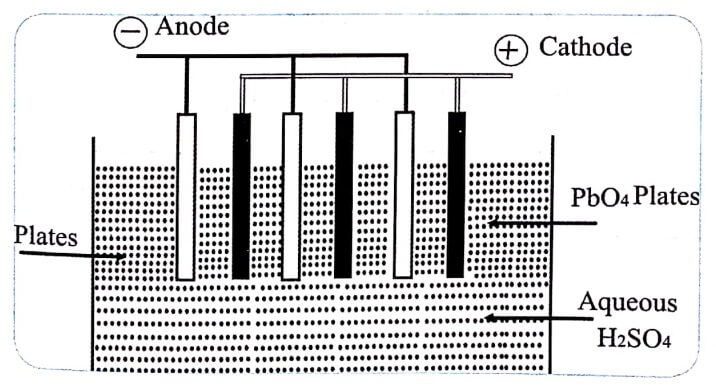
Fig (1) Lead acid battery
Working (discharging):
The electrode reactions that occur during the discharge of the cell, i.e. when current is drawn from the cell are as follows :
At anode:
At the negative pole (anode) oxidation of lead takes place. Then the lead ions combine with sulphate ions to produce lead sulphate.
Pb(s) → Pb2+(aq) + 2e–
Pb2+(sq) + SO42-(aq) → PbSO4(s)
___________________________________________
Pb(s) + SO42-(aq) → PbSO4(s) + 2e– …….. eqn(1)
____________________________________________
At cathode:
The electrons released at anode flow to the positive pole (cathode), where reduction reaction takes place.
PbO2(s) + 4H+ + 2e– → Pb2+(aq) + 2H2O
Pb2+(aq)+ SO42-(aq) → PbSO4(s)
________________________________________________
PbO2(s)+ 4H+ + SO2-4 + 2e– → PbSO4 +2H2O …….eqn (2)
________________________________________________
Over all cell reaction during use :
(1) + (2) gives
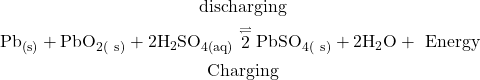
The PbSO4 formed get precipitated on the cathode and in the solution. When both anode and cathode are covered with PbSO4, the cell stops its functioning. So, the battery needs recharging.
The voltage of lead storage cell is 2.0 V and six such cells in the battery produces a total of 12 V.
Recharging the battery
Recharging is done by applying a voltage across the electrodes that is slightly higher than the voltage that the battery can deliver. When direct current is passed in this cell, the reaction is reversed.
As long as current is supplied to the battery, Pb2+ ions are reduced to lead metal while, at the PbO2 electrode, Pb2+ ions are oxidized to PbO2.
2 PbSO4(s) + 2 H2 O + Energy → Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4
During discharging the concentration of H2SO4 decreases, while the concentration of acid increases.
Maintenance:
If the lead-acid batteries are properly maintained in the following ways, they can function for long periods:
-
Avoid over discharging of the battery.
-
Avoid over heating of the battery.
-
Electrolyte level must be maintained by adding distilled water.
-
Wrong polarity connection during charging causes a permanent damage to the battery
Uses :
-
Lead acid storage cells are used in automobiles to supply current.
-
It is also used in Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS), as a powersystem whichprovide current constantlywithoutabreak.
-
They are also used in telephone exchanges, hospitals, power stations, railway stations etc.
Advantages and disadvantages of lead-acid battery
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 1. It produces very high current. | 1. Acid spillage. |
| 2. Six cells can make a car battery. | 2. Pb is toxic which is an environmental concern. |
| 3. Internal resistance is low. | 3. These batteries tend to slowly self-discharge. |
| 4. It is expected to function effectively for 300-350 cycles. | 4. The sulphuric acid becomes viscous when the temperature is very low, therefore flow of current gets reduced. |
| Read More Topics |
| An overview of primary alkaline battery |
| Important applications of wind energy |
| What is the basic theory of chemical kinetics? |





