The concept of length in physics is related to the concept of distance in everyday life. Length is defined as the distance between any two points in space. The SI unit of length is metre. The objects of our interest vary widely in sizes.
For example, large objects like the galaxy, stars, Sun, Earth, Moon etc., and their distances constitute a macrocosm. It refers to a large world,
The Radian (rad): One radian is the angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle. The Steradian (sr): One steradian is the solid angle subtended at the centre of a sphere, by that surface of the sphere, which is equal in area, to the square of radius of the sphere in which both objects and distances are large.
On the contrary, objects like molecules, atoms, proton, neutron, electron, bacteria etc., and their distances constitute microcosm, which means a small world in which both objects and distances are small-sized.
Distances ranging from 10-5 m to 102 m can be measured by direct methods. For example, a metre scale can be used to measure the distance from 10-3 m to 1 m , vernier calipers up to 10-4 m , a screw gauge up to 10-5 m and so on. The atomic and astronomical distances cannot be measured by any of the above mentioned direct methods. Hence, to measure the very small and the very large distances, indirect methods have to be devised and used. In Table a list of powers of 10 (both positive and negative powers) is given. Prefixes for each power are also mentioned. These prefixes are used along with units of length, and of mass.
Prefixes for Powers of Ten:
| Multiple | Prefix | Symbol | Sub multiple | Prefix | Symbol |
| 101 | deca | da | 10–1 | deci | d |
| 102 | hecto | h | 10–2 | centi | c |
| 103 | kilo | k | 10–3 | milli | m |
| 106 | mega | M | 10–6 | micro | µ |
| 109 | giga | G | 10–9 | nano | n |
| 1012 | tera | T | 10–12 | pico | p |
| 1015 | peta | P | 10–15 | femto | f |
| 1018 | exa | E | 10–18 | atto | a |
| 1021 | zetta | Z | 10–21 | zepto | z |
| 1024 | yotta | Y | 10–24 | yocto | y |
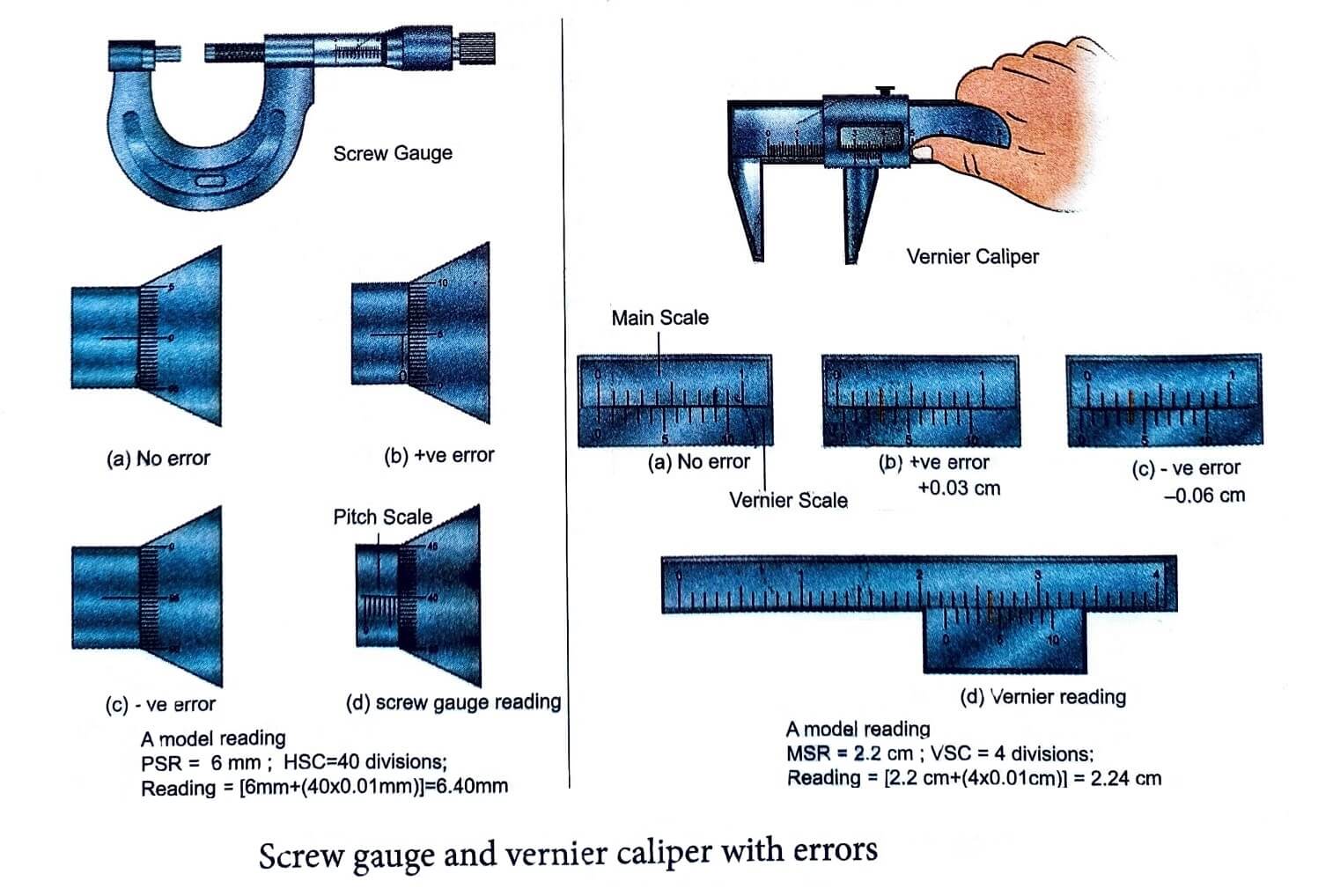
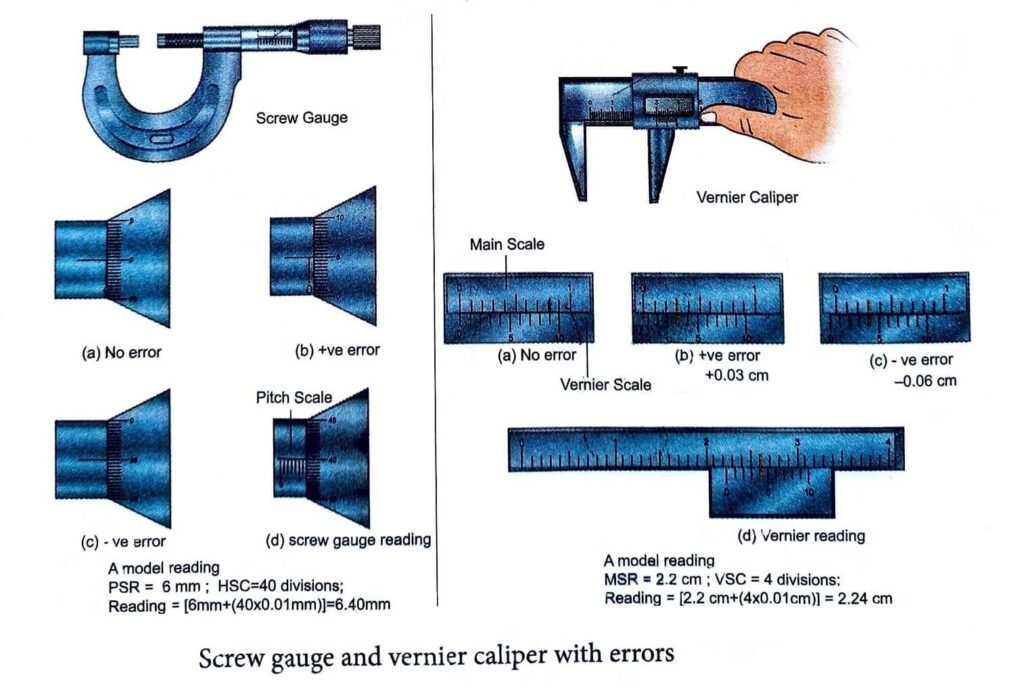
i) Measurement of small distances: screw gauge and vernier caliper Screw gauge: The screw gauge is an instrument used for measuring accurately the dimensions of objects up to a maximum of about 50 mm The principle of the instrument is the magnification of linear motion using
the circular motion of a screw The least count of the screw gauge is 0.01 mm Vernier caliper: A vernier caliper is a versatile instrument for measuring the dimensions of an object namely diameter of a hole, or a depth of a hole. The least count of the vernier caliper is 0.01 cm
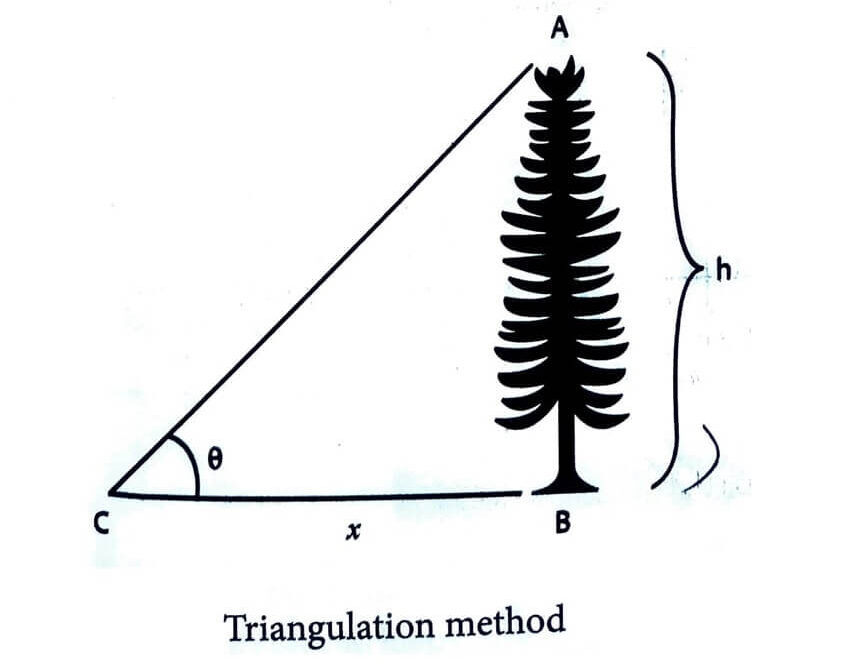
ii) Measurement of large distances : For measuring larger distances such as the height of a tree, distance of the Moon or a planet from the Earth, some special methods are adopted. Triangulation method, parallax method and radar method are used to determine very large distances.
Triangulation method for the height of an accessible object
Let AB = h be the height of the tree or tower to be measured. Let C be the point of observation at distance x from B. Place a range finder at C and measure the angle of elevation, ![]() as shown in Figure
as shown in Figure
height h = x tan θ
Knowing the distance x , the height h can be determined.
| Read More Topics |
| Hard and soft magnetic material |
| Charge densities in a semiconductor |
| Mobility and conductivity in semiconductors |