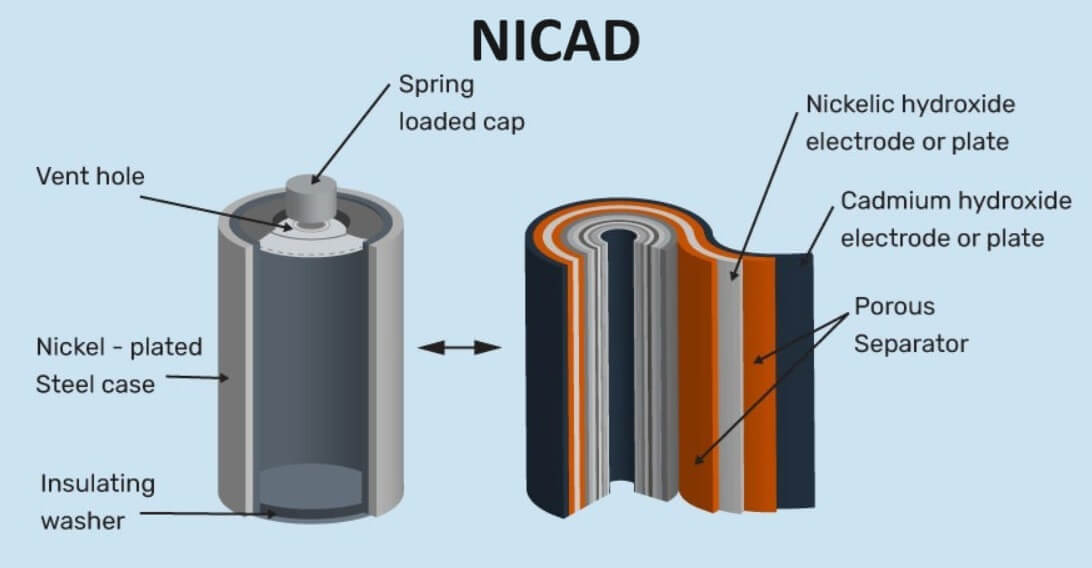
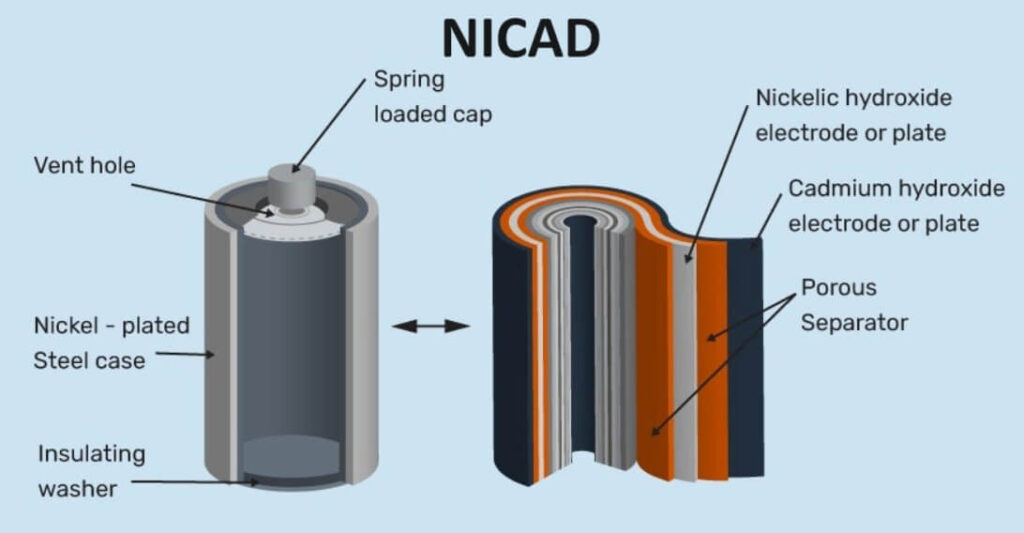
A nickel – cadmium battery is a type of alkaline storage battery. This is also a rechargeable battery. In a Ni – Cad cell, the anode is a cadmium electrode and the cathode is nickel oxide (NiO2). The electrolyte is a solution of KOH. The electrode and electrolytes are enclosed in a sealed container.
It is represented as:
Cd | Cd(OH)2 || KOH |NiO2 | Ni
Discharging:
The NICAD battery operates when, cadmium is oxidised to Cd2+ ions and insoluble Cd(OH)2 is formed. Ni2+ ions then combine with OH–ions to form Ni(OH)2.
At Anode : Cd(s) + 2OH–(aq) ⇌ Cd(OH)2(s) + 2e–
Recharging the battery
The recharging process is similar to lead storage battery. When the current is passed in the opposite direction, the electrode reaction gets reversed. So, Cd gets deposited in the anode and NiO2 in the cathode.
The net reaction during charging is :
Energy
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 1. It has longer life. | 1. It is very expensive. |
| 2. It has relatively high rates of discharge and recharge | 2. Cadmium is highly toxic |
| 3. It has ability to operate in low temperature. | – |
| 4. It is compact and lighter and used in high current applications. | – |
Uses:
- It is used in industrial trucks, emergency power applications and communication equipments.
- It is used in electronic calculators, etc.
- Due to low temperature performance it is widely used in aircraft and space satellites.
| Read More Topics |
| Lead acid batteries – Secondary Batteries |
| An overview of primary alkaline battery |
| Important applications of wind energy |