The word ‘Photonics’ is derived from the Greek word “Photos” meaning light. Photonics is the technology that deals with the generation, manipulation, transport, detection, and use of light energy, whose quantum unit is photon. Photons carry information through fibre optic cable, retrieve information in laser radar and other sensor devices, and can transport light energy. (laser machining and laser surgery).
Photonics as a field began with the invention of the first laser namely ruby laser in 1960 demonstrated by Dr. T.H. Maimann.
The term LASER is an acronym which stands for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation“. It is a source that produces an intense, concentrated and highly parallel beam of coherent light.
Properties of Laser
The most important properties of laser light are :
- It is high directional
- It is strongly intense
- It is extraordinary monochromaticity and
- It has high degree of coherence.
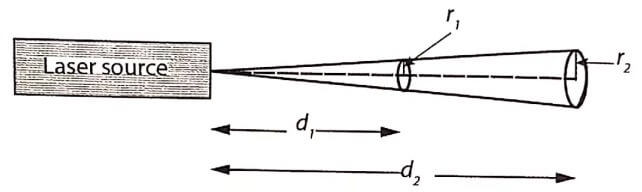
i. Directionality
The laser beam is highly directional. But ordinary light spreads in all directions. The divergence (angular spread) of the laser beam is very small. For a typical laser beam the angular spread is 1 mm/m but for an ordinary light source the angular spread is 1 m/m.
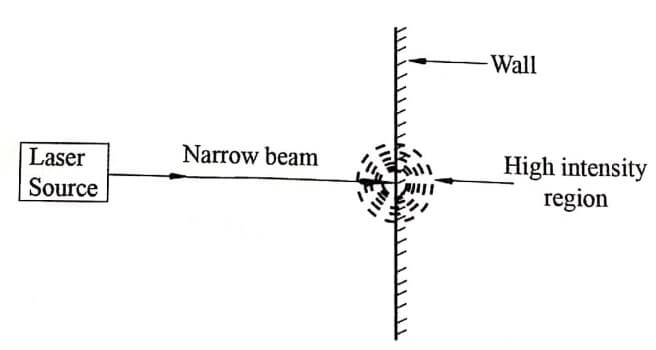
ii. Intensity
The intensity of the laser beam is very high. An ordinary source emits light uniformly in all directions. But laser emits light into a narrow beam and its energy is concentrated in a small region.
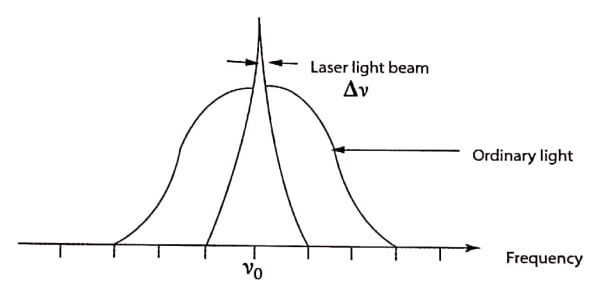
iii. Monochromaticity
The laser beam is highly monochromatic (single wavelength) than any other conventional monochromatic source. Ordinary light spreads over a wide range of frequencies of thousands of mega cycles per second, whereas the spread of the laser light is too small. The monochromaticity of conventional source is poorer than the laser source. (Fig.1.3).
iv. Coherence
A predictable correlation of the amplitude and phase at any one point with any other point is called coherence. The degree of coherence of laser beam is higher than that of the other conventional sources. The light from the source consists of wave trains, which are identical in phase and directions of propagation.
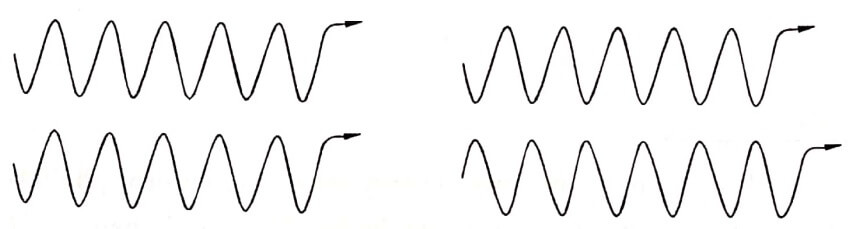 In-Phase Out of phase by 180°
In-Phase Out of phase by 180°
Fig. 1.4 Coherence
| Read More Topics |
| Basic components of a laser |
| Different types of scans |
| Magnetostriction oscillator method |





