Principle
The piezoelectric method of producing ultrasonic waves is based on the principle of Inverse piezo – electric effect.
Here, ultrasonic waves are produced when the frequency of the applied alternating voltage is equal to the vibrating frequency of the crystal.
Construction
- A slice of quartz crystal is placed between the metal plates A and B so as to form a parallel plate capacitor with the crystal as a dielectric.
- The two metal plates are connected with an induction coil L3 of the transformer.
- There are two more induction coil L1 and L2 .
- The coil L2 is connected a variable capacitor C1 which they combined to form a tank circuit or oscillatory circuit.
- The tank circuit and induction coil L1 are connected with a NPN transistor.
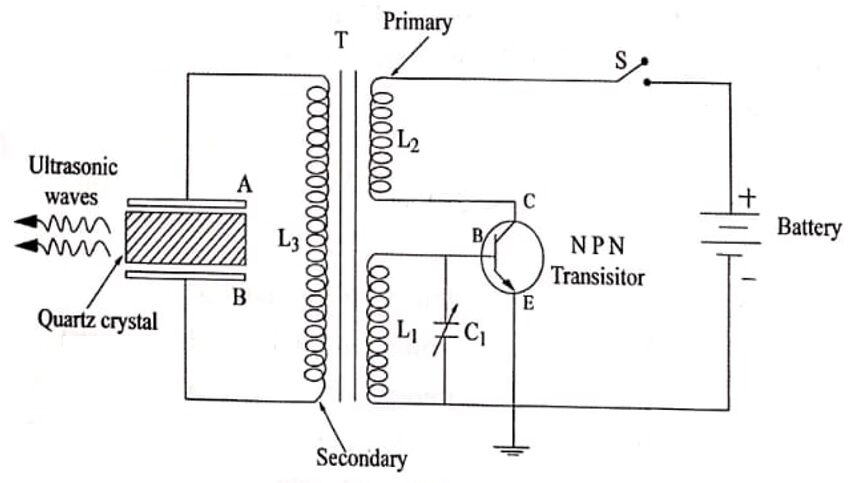
Fig. 1.1 Piezo-electric oscillator
Working
- When the battery is switched on, the electronic oscillator produces high frequency oscillations given by,
![]()
- The current is passed through the primary coils L1 and L2 of the circuit.
- This current is transferred to the secondary coil L3 of the circuit. Now oscillatory e.m.f. is induced in the coil L3 due to transformer action.
- Due to the principle of inverse piezo electric effect the crystal starts vibrating along the mechanical axis of the crystal.
- The frequency of the oscillator circuit is adjusted by the variable capacitor C1 and when this frequency is equal to the frequency of the vibrating crystal resonance occurs.
- At resonance the crystal vibrates large amplitude and ultrasonic waves are produced along both ends of the crystal.
- The fundamental (natural) frequency of the quartz specimen is given by
![]()
Where,
l- length of the material
E – Young’s modulus of the material
ρ- density of the material and
P – 1,2,3….etc., for fundamental, first overtone, second overtone etc.
E – Young’s modulus of the material
ρ- density of the material and
P – 1,2,3….etc., for fundamental, first overtone, second overtone etc.
Condition for resonance
Frequency of oscillatory circuit = Frequency of vibrating crystal
Advantages
i. Ultrasonic frequencies as high as 500MHz can be generated.
ii. The output power is high.
iii. The output power is independent of temperature and humidity.
iv. It can produce longitudinal as well as transverse ultrasonic waves.
v. It is more efficient than magnetostriction oscillator.
vi. The width of the resonance curve is so small and so we can get a stable and constant frequency of ultrasonic waves.
ii. The output power is high.
iii. The output power is independent of temperature and humidity.
iv. It can produce longitudinal as well as transverse ultrasonic waves.
v. It is more efficient than magnetostriction oscillator.
vi. The width of the resonance curve is so small and so we can get a stable and constant frequency of ultrasonic waves.
Disadvantages
- The cost of the quartz crystal is very high.
- Cutting and shaping the crystal are very complex.
- Preparation of the thin piezo-electric crystal is not easy.
| Read More Topics |
| Ohm’s Law |
| Introduction of ultrasonic sound waves |
| Fleming’s right hand rule |





