Introduction Principles of Management
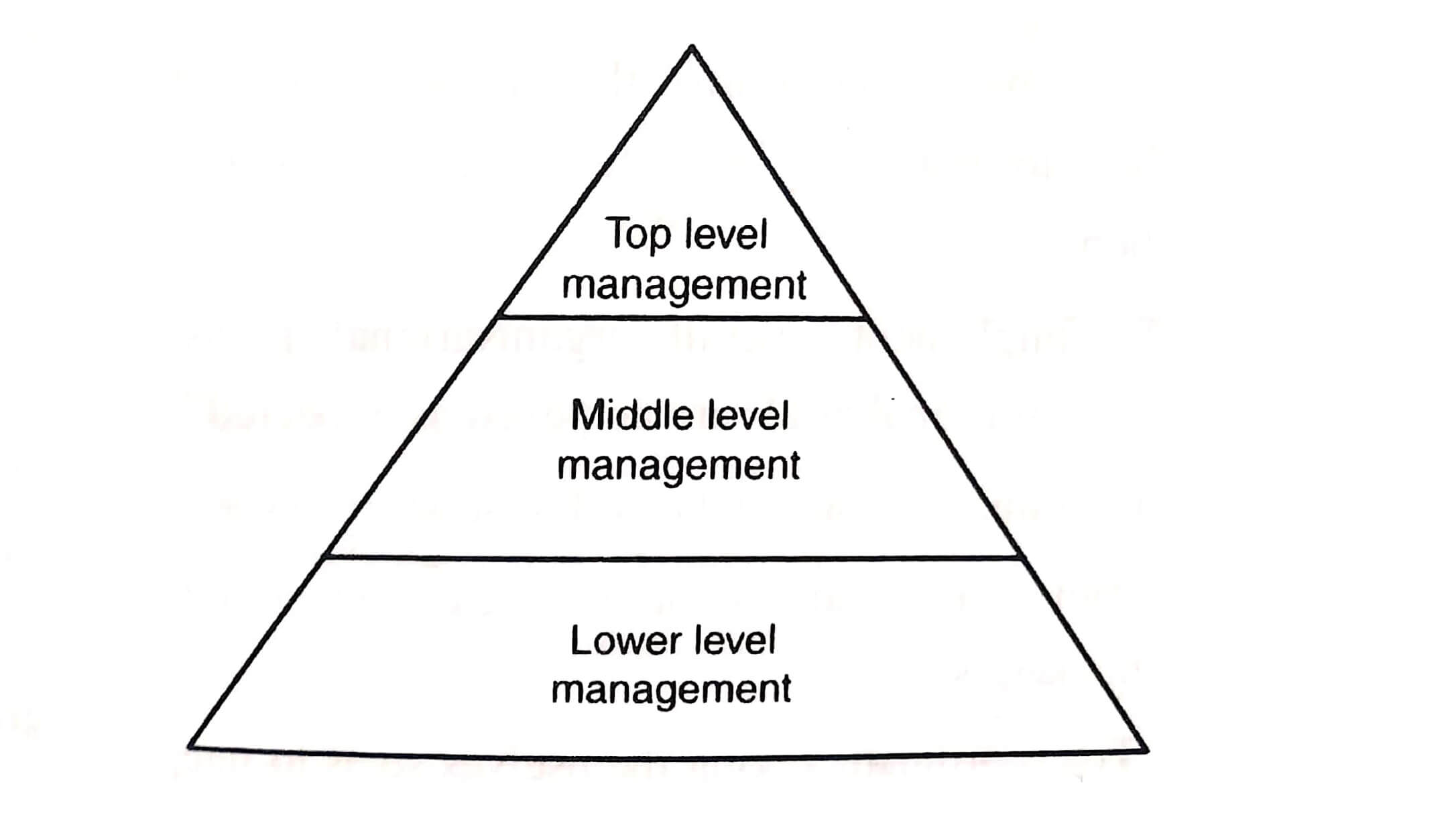
Principles of Management Every organization, regardless of size, type, or location, needs managers who have a variety of characteristics. No matter, what type of organization they work, managers are generally responsible for a group of individual performance. The relationship between managers and workers has changed as compared to the older master-servant relationship which makes the organization’s management more complex. A manager is someone who works with and through other people by coordinating their work activities in order to accomplish organizational goals. Managers may have a variety of titles and roles. They perform various jobs and duties and are responsible for higher profits and for great performance. Managers work in various departments and are employed by many types of organization. As leaders, managers must encourage this group to reach common business goals, such as bringing a new product to market in a timely fashion.
ROLES OF MANAGER
Henry Mintzberg describes a set of ten roles that a manager performs. These roles fall into three categories:
Interpersonal roles are roles that involve people (subordinates and persons outside the organization) and other duties that are ceremonial and symbolic in nature. The three interpersonal roles include:
Figurehead role : Perform ceremonial and symbolic duties, such as greeting visitors and signing legal documents
Leader
- Direct and motivate subordinates
- Counsel and communicate with subordinates
- Responsible for staffing and training
Liaison
Maintain information links both inside and outside organization via mail, phone calls, and meetings
Informational roles involve receiving, collecting, and disseminating information. The three informational roles include:
Monitor
- Seek and receive information
- Scan periodicals and reports
- Maintain personal contact with stakeholders
Disseminator
It is forward information to organization members, via memos, reports, and phone calls.
Spokes person
Transmit information to outsiders via reports, memos, and speeches.
Decisional roles revolved around making choices. The four decisional roles include entrepreneur, disturbance handler, resource allocator, and negotiator.
Entrepreneur
Initiate improvement projects; identify new ideas and delegate idea responsibility to others.
Disturbance handler
Take corrective action during disputes or crises; resolve Conflicts among subordinates; adapt to environments.
Resource allocator
Decide who gets resources; prepare allocator budgets; set schedules and determine priorities.
Negotiator
Represent department during negotiations of union contracts, sales, purchases, and budgets. Simply speaking, management is what managers do. Management is important for our society, industry and government organizations.
Management is as an art and science of getting work done through people. It is the process of giving direction and controlling the various activities of the people to achieve the objectives of an organization. The process represents the ongoing functions of primary activities engaged by managers. These functions are typically labeled planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. It can be easily remembered by POLC.
Definition of Management
Management may be defined in many different ways. Many eminent authors on the subject have defined the term “management”, some of these definitions are reproduced below:
Koontz and weihrich define management in a simple form as: “Management is the process of designing and maintaining an environment in which individuals working together in groups, efficiently accomplish selected aims”.
According to F. W. Taylor – “Management is the art of knowing what you want to do and then seeing that it is done in the best and cheapest way”.
In the words of S. George “Management consists of getting things done through others. Manager is one who accomplishes the objectives by directing the efforts of others”. McFarland defines the management in a more elaborate form as: “Management is defined for conceptual, theoretical and analytical purposes as that process by which managers create, direct, maintain, and operate purposive organization through systematic, coordinated co-operative human effort”. In the words of George R. Terry
“Management is a distinct process consisting of planning, organizing, actuating and controlling performed to determine and accomplish the objectives by the use of people and resources”. In the words of Henry Fayol – “To manage is to forecast and to plan, to organize, to command, to co-ordinate and to control”.
According to Newman, Summer and Warren – “The job of management is to make cooperative endeavour to function properly. A manager is one who gets things done by working with people and other resources”.
According to John, F.M. – “Principles of Management may be defined as the art of securing maximum results with a minimum of effort so as to secure maximum results with a minimum of effort so as to secure maximum prosperity and happiness for both employer and employee and give the public the best possible service”.
From the definitions quoted above, it is clear that the management is the process of coordinating and integrating work activities so that they are completed efficiently and effectively with and through other people. Management is a continuous process. Management aims at achieving the organizations goals by ensuring effective use of resources.
Nature of Principles Management
An analysis of the various definitions and contributions to the field of management by eminent philosophers and authors indicates that the management has certain nature/characteristics.
The following are the salient characteristics of management:
Management is multidisciplinary in nature
Management is an interdisciplinary study. It draws ideas and concepts from various disciplines, such as economics, statistics, mathematics, psychology, sociology, anthropology etc.
Management is a continuous process
Management is a process, function or activity. This process continues till the objectives set by administration are actually achieved.
Management is a universal activity
Management is not applicable to business undertakings only. It is applicable to political, social, religious and educational institutions also. Management is necessary when group effort is required.
Management is a Science as well as an Art
Management is an art because there are definite principles of management. It is also a science because by the application of these principles predetermined objectives can be achieved.
Management is dynamic and not static
The principles of management are dynamic and not static. It has to adapt itself according to social changes.
Management is a Profession
Management is gradually becoming a profession because there are established principles of management which are being applied in practice, and it involves specialized training and is governed by ethical code arising out of its social obligations.
Management is a group activity
Management comes into existence only when there is a group activity towards a common objective. Management is always concerned with group efforts and not individual efforts. To achieve the goals of an organization managing plans, organizes, co-ordinates, directs and controls the group effort.
Management aims at obtaining wealthy results
Manager’s primary job is to the productive assure performance through planning, direction and control. It is expected of the management to bring into being the desired
Scope of Management
It is difficult to precisely state the scope of management, However, the management includes the following scopes:
(i) Functional areas of management:
Financial Managers includes forecasting, cost control, manage accounting, budgetary control, statistical control, financial planning etc.
Human Resource Management covers the various aspects relating to the employees of the organization such retirement, as recruitment, training, transfers, promotions, terminations, remuneration, labor welfare and social security, industrial relations etc.
Marketing Managers deals with marketing of goods, sales promotion, advertisement and publicity, channels of distribution, market research etc. Production Managers includes production planning, quality control and inspection, production techniques etc. Material Management includes purchase of materials, issue of materials, storage of materials, maintenance of records, materials control etc. Purchasing Management includes inviting tenders for raw materials, placing orders, entering into contracts etc. Maintenance Management relates to the proper care and maintenance of the buildings, plant and machinery etc.
Functions of Management
- Planning
- Organizing
- Staffing
- Directing
- Controlling
- Planning
Planning, in simple, is looking ahead. It is the process of preparing for the future. Effective planning leads to efficient managers. Effective planning provides answers to questions such as – What to do? When to do? How to do? Who is to do?
The planning process involves the following activities:
- Determination of the goal of the organization.
- Formulating policies, rules, procedures etc. for the organization.
- Forecasting the future based on past and present activities.
Organizing – Principles of Management
Organizing establishes harmonious relationship among all workers of an organization by providing them with suitable authority and responsibility.
According to Louis A. Allen “Organization involves identification and grouping the activities to be performed and dividing them among the individuals and creating authority and responsibility relationships among them for the accomplishment of organizational objectives”. Organization process involves the following activities:
- Identification and analysis of activities required for the attainment organizational objectives.
- Assignment of duties to the individuals concerned.
- Follow-up the activities.
Staffing
Staffing process involves selecting candidates for positions, fixing salary, training and developing them for effective organizational functions. The manager performs the duties of job analysis, job description etc. which come under the staffing function.
Directing / Leading
Directing involves activities, such as guiding, supervising. communicating and motivating the subordinates in their jobs. Motivation, leadership and communication are three. Important sub functions of directing. Motivation helps to increase the performance of workers. Communication provides with a proper information to the subordinates for the improved and effective managers. Leadership is the process by which a manager guides and influences the work of his subordinates.
Benefits of Scientific Management
The benefits of scientific management are:
- Replacement of traditional rule of thumb method by scientific techniques.
- Proper selection and training of workers.
- Incentive wages to the workers for higher production.
- Elimination of wastes and rationalization of system of control.
- Standardization of tools, equipment, materials and work methods.
- Detailed instructions and constant guidance of the workers.
- Establishment of harmonious relationship between the workers.
- Better utilization of various resources.
- Satisfaction of the needs of the customers by providing higher quality products at lower prices.
Fayol’s Administrative Management Theory
Whereas scientific management focused the on productivity of individuals, the administrative management theory concentrates on developing organizational structure that leads to high efficiency and effectiveness. Organizational structure is the system of task and authority relationships that control how employees use resources to achieve the organization’s goals. The emphasis is on the development of managerial principles rather than work methods. Henry Fayol was the most important exponent of this theory.
Henri Fayol (1841-1925) – Principles of Management
A French mining engineer, identified 14 principles of management based on his manage experiences. He believed that these principles are essential to increase the efficiency of the management process. These principles provide modern-day managers with general guidelines on how a supervisor should organize her department and manage her staff. Henry Fayol is considered the further of modern theory of general and industrial management. Although later research has created controversy over many of the following principles, they are still widely used in management theories.
Fayol’s contributions arc published in his famous book “The general and industrial administration”. Fayol’s famous book falls into two parts. The first part concerned with the theory of administration in which Fayol divided the total industrial activities into six categories which are given below:
- Technical (Production, Manufacture).
- Commercial (Buying, Selling, Exchange).
- Financial (Search for and optimum use of capital).
- Security (Protection of property and persons).
- Accounting (Balance sheets, Cost statistics).
- Management (Planning, Organizing, Coordinating, Directing, Controlling)
The second part is concerned with the fourteen principles of manage. They are:
- Division of work
- Authority and Responsibility
- Discipline
- Unity of command
- Unity of Direction
- Subordination of individual interest to general interest
- Remuneration of personnel
- Centralisation
- Scalar chain
- Order
- Equity
- Stability of tenure of personnel
- Initiative
- Esprit de corps.
- Division of work
Work should be divided in a proper way with reference to the available time. In general worker on the same job and the managers on the same duty acquire ability sureness and accuracy which increase their output.
Authority and Responsibility
Authority: It is the power given to a person to get work from his subordinates.
Responsibility: It is the kind and amount of work expected of from a man by his superior. One of the essential elements of a good management is delegation of authority to the lower levels of management and fixing responsibility on its own.
Discipline
Discipline is essential for the smooth running of organization. To Fayol, discipline will result from good leadership at all levels of the organization, fair agreements and judiciously enforced penalties for infractions.
Unity of command
An employee must receive orders and instructions from one supervisor only. Multiple commands will cause conflicts and confusions. A sound management should avoid dual commands.
Unity of Direction
Unity of direction signifies each group of activities having the same objective with one head and one plan. All the groups should coordinate and work together to achieve the common goal.
Subordination of individual interest to general interest
Every employee is working in an organization and his interest is to earn money to meet his personal needs. The general interest of the organization is the development and the progress of the organization.
The employees should give importance first to the general interest than his individual interest. It will lead to effective management of the organization.
Remuneration of personnel
Remuneration should be fair for both the employees and employers. The wage payment systems should satisfy the employees.
Centralisation
The organization is centralized when the power is concentrated with one person. If the power is fully distributed to the subordinates, the organization is fully decentralized. For effective manage of people decentralization is necessary. Decentralization helps to take a quick decision on all important problems.
Scalar chain
Scalar chain principle states that instructions and orders should be sent from the top manage to the bottom management.
Order
Two types of order 1) Materials order 2) Social order.
In any organization materials and for men are provided in correct places so that materials can be easily taken out and men easily located and also saved time. Materials order: “A place for everything and everything in its place”.
Social order: “A place for everyone and everyone in its place”.
Equity
Equity refers to the treatment of employees equally. Equal treatment of the employees helps to achieve organizational goals.
Stability of staff
A high employee turnover rate is not good for the efficient functioning of any organization.
Initiative
It is concerned with thinking and execution of a plan. When employees come forward with new ideas, they must be encouraged by the superiors. It will create the morale of the employees.
Esprit-de-corps
This means union is strength. In organization, employees should be harmony and unity. It improves the employee morale.