Functions of SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition)
The supervisory control and data acquisition systems allow a few operators to monitor the generator. The following are the functions of SCADA.
1. Data Acquisition : It provides telemetered measurements and status information to operator.
2. Information display (limit violations, unplanned events).
3. Supervisory control (CBs (Circuit Breakers) : On/Off ; Generator: stop/start, raise/lower command)
(a) Electrical breaker control.
(b) Voltage regulation.
(c) Tap changer control.
(d) Capacitor control.
(e) Loss reduction.
(f) Miscellaneous device control.
(g) Load management.
(h) Fault isolation.
(i) Service restoration.
4. Information storage and results display. Reports such as energy accounting, reserve calculation, interchange evaluation.
5. Sequence of events acquisition.
6. Remote terminal unit processing.
7. General maintenance.
8. Runtime status verification.
9. Economic modelling.
10. Remote start / stop.
11. Load matching based on economics.
12. Load shedding : Provides both automatic and operator-initiated tripping of load in response to system emergencies.
Logging
-
- Data is stored in compressed format.
- Logging / archiving can be frequency or event driven.
- Logs all operator entry, alarms for selected information.
- Logging of user actions together with user ID.
- VCR facility for playback of stored data.
General Functions of Archiving Unit
-
- Invert or add zero symbols to existing library.
- Interface new peripherals (printer, plotter.)
- Define operators and select their system access rights.
- Download new configurations into RTU.
- Modify logbook and list appearance.
Substation control Functions of SCADA
The substation control functions of SCADA are:
- Alarm functions
- Control and indication.
- Control of position of devices.
- Data collections.
- Protective functions.
- Control and monitoring functions.
Other Functions of SCADA and EMS are:
- Network topology determination.
- State Estimation.
- Security analysis and control
SECURITY ANALYSIS AND CONTROL
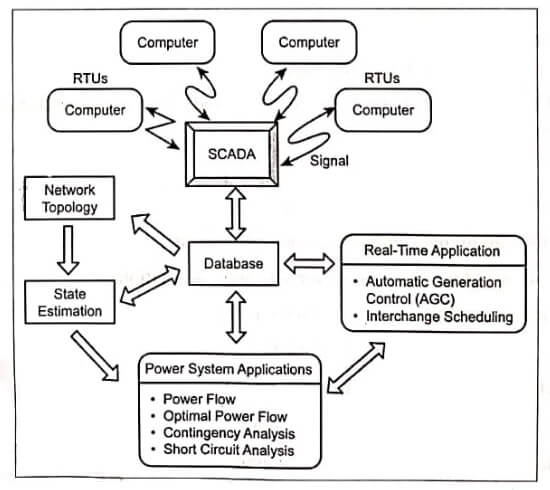
The Security monitoring is the on-line identification of the actual operating conditions of a power system. It requires system-wide instrumentation to gather the system data as well as a means for the online determination of network topology involving an open or closed position of circuit breakers. A state estimation has been developed to get the best estimate of the complex bus voltage at any instant from the redundant set of telemetered data and breaker status. The state estimation
provides the database for security analysis as shown in image. The estimated values are then checked against the overload limits. If no limit is violated, output of the estimator may be used for contingency evaluation. Hence overload limits are reached, suitable remedial measures help the operator to choose between rescheduling, line switching and load shedding.