Definition : Shape memory alloys are special type of alloys that have the ability to return to a original defined shape when heated.
Shape memory alloys are also called as smart materials (or) intelligent materials (or) active materials.
The shape memory transformation was first observed by Chang and Read in 1932.
Examples of SMA’s
| a) Au – Cd alloy | b) Ti – Ni alloy | c) Mn – Cu alloy |
| d) Ni – Mn – Ga alloy | e) Cu – Al – Ni alloy |
Transformation temperature
The range of temperature at which the SMA switches from new shape to its original shape is called transformation temperature (or) memory transfer temperature.
Below the transformation temperature the SMA can be bent into various shapes. Above the transformation temperature the SMA returns to its original shape. This change in shape was mainly caused due to the change in crystal structure (phase) within the materials, due to the rearrangement of atoms within itself.
Properties of SMA
SMA’s are metal alloys which exhibit following two unique properties
- Shape Memory Effect
- Pseudo elasticity (or) Super elasticity
Phases (Structures) of SMA
In general the SMA has two phases (crystal structures) viz.,
(i) Martensite and
(ii) Austenite
Martensite
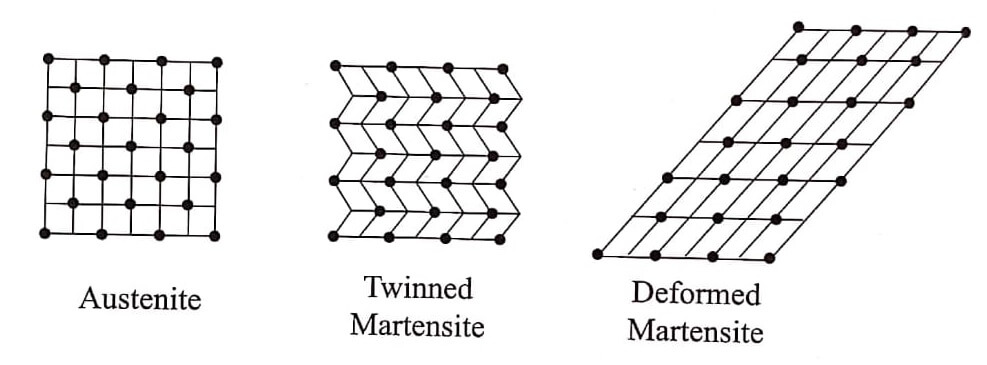
The martensite is a low temperature phase. It is a soft and easily deformable phase. Martensite structure have two forms viz.,
- Twinned martensite before loading and
- Deformed martensite after loading.
Austenite
The austenite phase is a stronger phase of shape memory alloy. It occurs at high temperature It has cubic structure.
Working of SMA
The macroscopic view of austenite and twinned martensite has no difference in its shape, whereas differences can be observed only in the microscopic scale. The austenite is a cubic, whereas the martensite is a twinned structure. Martensite is easily deformed by applying stress. The deformed martensite is shown in Figure.
Types of SMAs
Generally the SMAs are classified into two as
- One-way shape memory
- Two-way shape memory
One-way shape memory
The materials which exhibit shape memory effect (i.e., taking their own shape) only upon heating are said to have one way shape alloy.
Two-way shape memory
The materials which exhibit shape memory effect both during heating and cooling are said to have two-way shape memory.
| Read More Topics |
| Properties of metallic glasses |
| Conducting materials-solved problems |
| Ferro electricity and applications |





