Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is the application of standard business practices to building software applications. It’s typically divided into six to eight steps: Planning, Requirements, Design, Build, Document, Test, Deploy, Maintain.
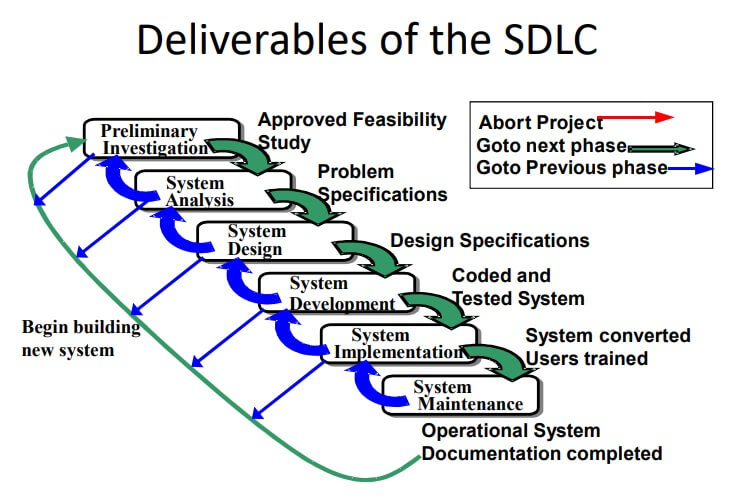
Six Phases of the System Development Life Cycle
- Preliminary Investigation
- Assesses feasibility and practicality of system
- System Analysis
- Study old system and identify new requirements
- Defines system from user’s view
- System Design
- Design new/alternative system
- Defines system from technical view
- System Development
- New hardware and software is acquired, developed, and tested
- System Implementation
- System installation and training
- System Operation & Maintenance
- Daily operation
- Periodic evaluation and updating
Preliminary Investigation – Software Development Life Cycle
Determine if a new system is needed
- Three primary tasks:– Define the problem
- By observation and interview, determine what information is needed by whom, when, where and why
- Suggest alternative solutions
- Prepare a short report
System Analysis
- In depth study of the existing system to determine what the new system should do.
- Expand on data gathered in Phase 1
- In addition to observation and interviews, examine:
- Formal lines of authority (org chart)
- Standard operating procedures
- How information flows
- Reasons for any inefficiencies
System Analysis Documentation Produced
Complete description of current system and its problems
- Requirements for new system including:
– Subject
– Scope
– Objectives
– Benefits - Possible development schedule
System Design
- Uses specifications from the systems analysis to design alternative systems
- Computer – Aided Software Engineering (CASE) tools are software based products designed to help automate the production of information systems.
Examples:
– Diagramming Tools
– Data Repositories
– Prototyping Tools
– Test Data Generators
– Documentation Tools
– Project Management Tools
System Design Documentation Produced
- System Design Report
– Describe Alternatives including:- Inputs/Outputs
- Processing
- Storage and Backup
- Recommend Top Alternative based upon:
- System Fit into the Organization
- Flexibility for the future
- Costs vs. benefits
System Development
- Build the system to the design specifications
- Develop the software
- Purchase off the shelf software OR
- Write custom software
- Acquire the hardware
- Test the new system
- Module (unit) test – tests each part of system
- Integration testing – tests system as one unit
- Create manuals for users and operators
System Implementation
- Convert from old system to new system
- Train users
- Compile final documentation
- Evaluate the new system
Operations & Maintenance
- Types of changes:
– Physical repair of the system
– Correction of new bugs found (corrective)
– System adjustments to environmental changes
– Adjustments for users’ changing needs (adaptive)
– Changes to user better techniques when they become available (perfective) - Evaluation Methods
– Systems audit – performance compared to original specifications
– Periodic evaluation – “checkups” from time to time, modifications if necessary
Advantages of Software Development Life Cycle SDLC
Increase
• Development speed
• Product Quality
Improve
• Tracking & Control
• Client relation
Decrease
• Project risk & Project management overhead
| Read More Topics |
| Control System Engineering |
| Central Processing Unit |
| Software product and process |
| Agility and cost of change |
| The Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model |