SQUID stands for Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices. It is a double junction quantum interferometer formed from two Josephson junctions mounted on a superconducting ring. SQUID is based on the flux quantization in a superconducting ring. The total magnetic flux passing through the ring is quantized. It is used to detect very minute magnetic filed in the order of 10-14 tesla.
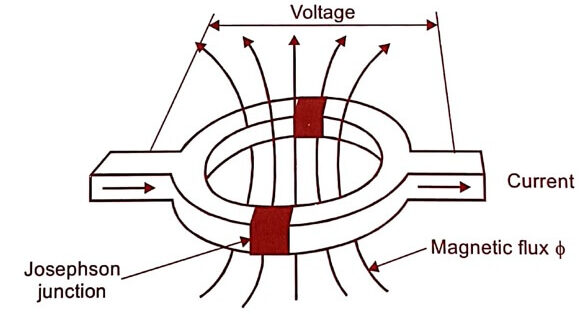
Fig 1.1
When the magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the plane of the ring, current is induced at the two Josephson junctions and produces interference pattern. The induced current flows around the ring, so that the magnetic flux in the ring can have quantum values of flux, which corresponds to the value of magnetic field applied.
- SQUIDs are used to detect the variation in very minute magnetic signals.
- SQUIDs are also used in the study of earth quakes, removing paramagnetic impurities, detection of magnetic signals from the brain, heart, etc.,
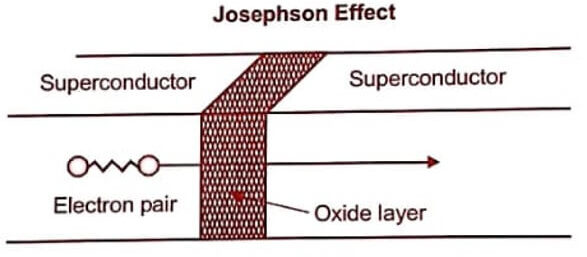
Fig 1.2. Josephson Effect
DC – Josephson Effect
- When two superconducting materials are separated by a thin layer of insulating material (oxide layer), then there is a DC current flows through the circuit in the absence of electric field or magnetic field.
- The gap is in the order of 50 A° – 100 A° .
AC Josephson effect
- When two superconducting materials are separated by a thin layer of insulating material, there is a microwave generated when it is connected with DC external voltage.
- Josephson devices are used to produce microwaves.
| Read More Topics |
| Applications of superconducting materials |
| Magnetic superconducting materials – Questions & Answer |
| Energy distribution of electrons in metals |





