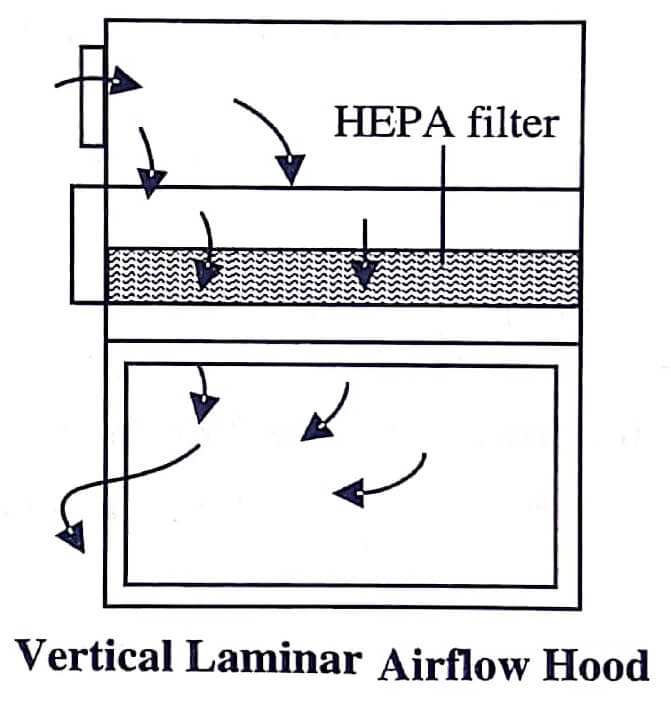
A laminar airflow hood is of two types:
Horizontal Airflow Hoods
These hoods (figure) sweep the filtered air from the back to the front of the hood. An electrical blower draws the contaminated room air using a pre-filter (similar to a furnace filter), to remove gross contaminants. The pre-filter demands timely cleanliness and replacement.
The air after passing through the pre-filter is accelerated (but not pressurised) so that a consistent airflow distribution reaches the final filter (HEPA filter), present at the back portion of the hood’s working area.
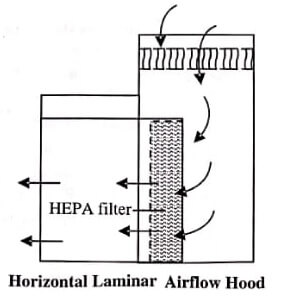
HEPA filter removes 99.97% of 0.3μ or larger sized particles, thus removing most of the 0.5μ or larger sized airborne microorganisms.
Vertical Airflow Hoods
These hoods (figure) sweep the filtered air vertically. The air passing through HEPA filter merges from the top and passes downward through the working area.
The vertical airflow hoods work on the principle that the air flow between the HEPA filter and the component used for CSPs preparation should not be interrupted. When a foreign object comes in between the sterile object and the HEPA filter, the wind turbulence (zone of turbulence) in the critical area increases, and foreign contaminants are carried to the sterile work surface, thus contaminating the injection port, needle, or syringe.
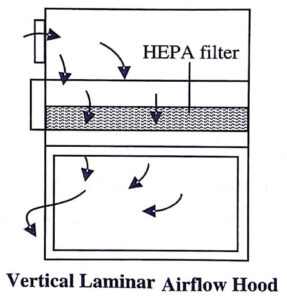
For ensuring complete sterility, nothing should pass behind a sterile object in a horizontal airflow hood; and in case of vertical airflow hood, nothing should pass above the sterile object. The materials within the compounding work area interrupt the pattern of air blowing from the HEPA filter.
[sc_fs_faq html=”true” headline=”h2″ img=”” question=”What are Vertical Airflow Hood?” img_alt=”” css_class=””] An item of laboratory equipment called a vertical airflow hood, also called a laminar flow hood, directs filtered air in a vertical direction to provide a controlled and sterile working environment. To avoid contamination and shield samples or equipment from exposure to airborne particles, it is frequently used in microbiology, pharmaceutical, and medical research. [/sc_fs_faq]
| Read More Topics |
| Citric acid utilization test |
| Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) |
| Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) |
| Single cell isolation methods |