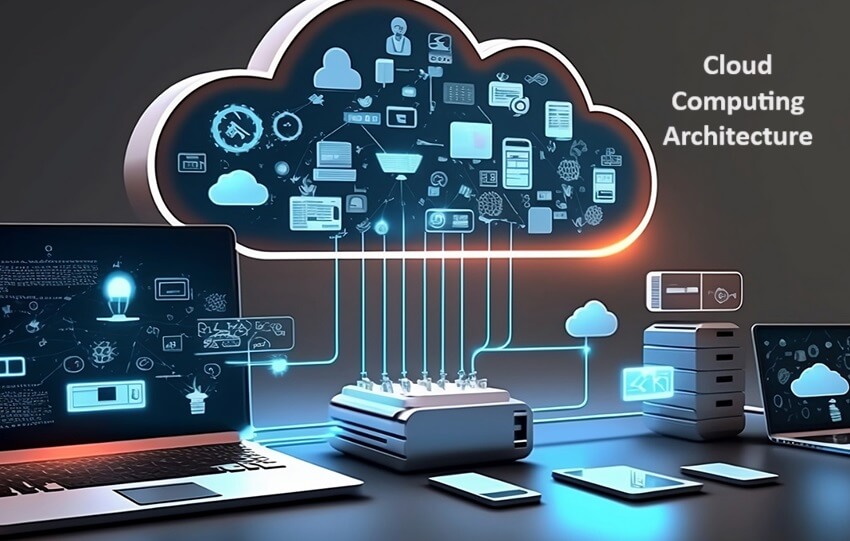
Cloud Computing Architecture: As cloud computing continues to revolutionize the way businesses operate, it’s crucial to understand the underlying architecture that supports these innovative technologies. Cloud computing architecture consists of six key components that work together seamlessly to deliver efficient and scalable solutions to users. These components include infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service (SaaS), security measures, scalability and flexibility, and data management.
Each component of cloud computing architecture plays a vital role in providing users with access to on-demand resources, applications, and services. Understanding how these components interact and support one another is essential for organizations looking to leverage the power of cloud computing effectively. By delving into the intricacies of cloud computing architecture, businesses can optimize their operations, enhance security measures, and effectively manage their data in the cloud.
What are the key components of cloud computing?
Cloud computing consists of several essential components that enable efficient data storage, processing, and accessibility. The key components are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – Provides virtualized computing resources like servers, storage, and networking.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) – Offers a framework for developers to build, test, and deploy applications.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) – Delivers ready-to-use software over the internet, such as Google Drive or Microsoft 365.
- Cloud Storage – Stores and manages data securely on remote servers.
- Cloud Security – Ensures data protection, encryption, and secure access controls.
These components work together to offer scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency in cloud computing.
Overview of Cloud Computing Architecture
Cloud computing architecture refers to the structure and design of the various components that make up a cloud computing system. This includes the networking infrastructure, servers, storage, virtualization layer, and the software that enables users to access and interact with cloud services. The architecture of a cloud computing system is crucial in determining its performance, scalability, and security.
At its core, cloud computing architecture is built on the principles of virtualization and abstraction. Virtualization allows physical hardware resources to be pooled together and divided into virtual instances, enabling multiple users to share the same underlying infrastructure. Abstraction, on the other hand, provides a layer of separation between the hardware and software components, allowing applications to run independently of the underlying hardware. These two principles form the foundation of cloud computing architecture, enabling organizations to maximize resource utilization, streamline operations, and adapt to changing business needs with ease.
Understanding the Role of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) plays a vital role in cloud computing architecture by providing virtualized computing resources over the internet. With IaaS, users gain access to virtual machines, storage, and networking components as a service, allowing for scalable and flexible infrastructure provisioning. This model enables organizations to avoid the costs associated with purchasing and maintaining physical hardware, thereby reducing capital expenditure and improving efficiency.

IaaS allows businesses to quickly deploy and scale resources based on their needs, offering a pay-as-you-go pricing model that aligns costs with actual usage. By abstracting the underlying infrastructure, IaaS simplifies the management and maintenance of IT resources, freeing up time and resources for core business activities. This level of abstraction also enhances security by centralizing control and enabling uniform security configurations across the infrastructure.
Exploring the Benefits of Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers a range of advantages to organizations seeking streamlined software development and deployment processes. With PaaS, businesses can leverage pre-built infrastructure and tools to accelerate the application development cycle, reducing time-to-market and overall costs. This allows development teams to focus more on innovation and less on managing underlying infrastructure, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
Another key benefit of PaaS is its scalability, which enables companies to easily adjust resources based on demand. This flexibility ensures that applications can handle fluctuations in usage without the need for manual intervention, providing a seamless experience for end-users. Additionally, PaaS offers a standardized environment for development, making it easier for teams to collaborate and share resources effectively. Such uniformity enhances consistency and reliability across projects, ultimately improving the overall quality of software deliverables.
The Importance of Software as a Service (SaaS) in Cloud Computing
Software as a Service (SaaS) plays a crucial role in cloud computing architecture, offering users accessibility to applications and software over the internet. This accessibility allows for easy deployment and management of software without the need for physical installation on individual devices. With SaaS, users can conveniently access a wide range of applications from anywhere with internet connectivity.

One of the key benefits of SaaS in cloud computing is its cost-effectiveness for both businesses and individual users. By subscribing to SaaS applications on a pay-as-you-go basis, users can avoid the high upfront costs associated with purchasing and licensing traditional software. This subscription model also allows for scalability, enabling users to easily adjust the number of subscriptions based on their requirements without being tied down to long-term contracts. Additionally, SaaS providers handle software maintenance and updates, ensuring that users always have access to the latest features and improvements.
Security Measures in Cloud Computing Architecture
Security measures in cloud computing architecture are crucial to ensure the safety and integrity of data stored in the cloud. Encryption plays a key role in safeguarding information, by converting data into a format that can only be deciphered with the appropriate decryption key. This protects data from unauthorized access and helps maintain confidentiality.
Another important security measure is authentication, which verifies the identity of users and devices before granting access to cloud resources. Through the use of strong authentication protocols, such as multi-factor authentication, cloud providers can ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data. Implementing robust authentication mechanisms is essential in preventing unauthorized users from compromising the security of cloud-based systems.
Scalability and Flexibility in Cloud Computing
One of the key advantages of cloud computing is its inherent scalability. This means that cloud resources can be easily adjusted based on fluctuating demands, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization. By dynamically allocating resources as needed, cloud computing allows organizations to scale up or down quickly without the limitations of traditional on-premise infrastructure.
In addition to scalability, cloud computing also offers flexibility in terms of resource allocation and management. With the ability to deploy and access resources on-demand, organizations can adapt to changing business requirements efficiently. This flexibility enables businesses to respond swiftly to market changes, innovate rapidly, and meet growing demands without being constrained by fixed infrastructure capacity.
Data Management in Cloud Computing Architecture
Data management in cloud computing architecture is a critical aspect that focuses on the organization, storage, and handling of data within a cloud environment. Data in the cloud is typically stored in virtualized pools of storage hosted by third parties, offering scalability and accessibility to users. With the use of data management tools and technologies, organizations can efficiently manage their data, ensuring its availability, reliability, and security.
One of the key benefits of data management in cloud computing architecture is the ability to easily scale storage resources based on the changing needs of the business. This scalability ensures that organizations can effectively store and manage large volumes of data without the need for significant upfront investments in physical infrastructure. Additionally, data management in the cloud allows for improved data protection through automated backups, robust security measures, and disaster recovery capabilities, mitigating the risk of data loss or breaches.
| Read More Topics |
| SQL knowledge for programmer and developers |
| What are the benefits of data science |
| Is Java good for automation? |