Nowadays, hydraulics and pneumatics power systems are the most widely used power systems in modern construction and manufacturing applications. Although both systems have many similarities, they also have many mechanical differences and specific industrial uses.
This article also explores the major differences between hydraulics and pneumatics and their uses. But before proceeding to their differences, first, we will try to understand what basically both they are;
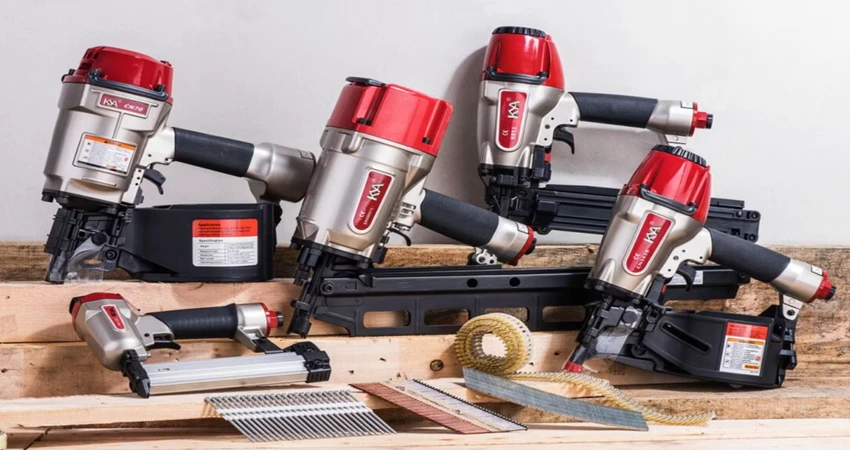
Pneumatic System
Pneumatic power flows pressurized air to create mechanical motion. It works on pressure rules and is supported by compressed air or gas. Different components, such as air tanks, standard cylinders, compressors, hoses, and transition lines, operate the pneumatic system.
Uses of Pneumatic System
- They play a major role in medicine (especially dentistry), food manufacturing, construction, robotics, mining mills, and pharmaceuticals.
- The basic purpose of Pneumatic is shock absorption as the compressed gas makes them less prone to damage from shocks.
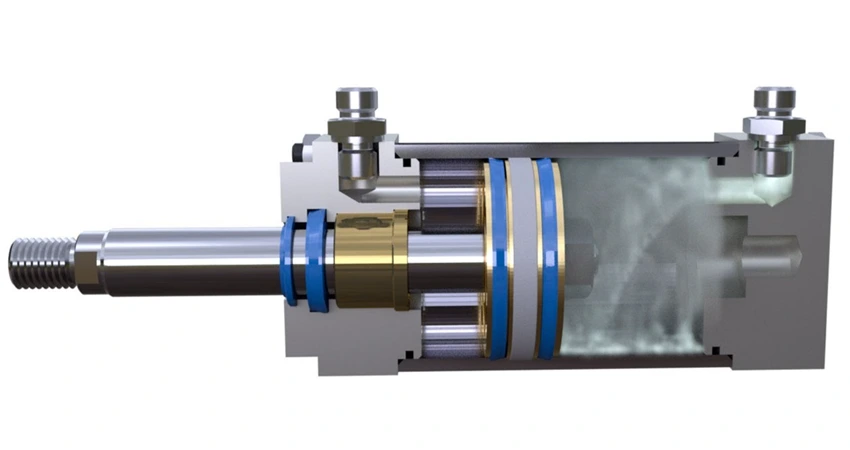
Hydraulic System
A hydraulic system shifts mechanical power into productive form while using pressurized liquids. Similar to pneumatic systems, it also depends on valves to control the velocity and power of actuators.
Uses of Hydraulic System
- Hydraulic systems are widely used to control oil leakage from valves or hoses, which prevents their use in oil-consumption systems.
- Hydraulic power covers different industrial uses, including elevators, dams, amusement parks, and hydraulic presses.
- They also work in turbines, aircraft wing flaps, wheelchairs, hydraulic lifts, etc.
Main Difference Between Hydraulics and Pneumatics
- The major difference that sets both systems apart is the usability of hydraulic liquids, which remains unchanged. On the other hand, pneumatic systems use gases that can compress.
- Hydraulics are larger but slower, while pneumatics are more compact and faster.
- Hydraulics systems provide greater power and precision. However, pneumatics deliver less force and accuracy.
Let’s see hydraulics and pneumatics differences at the broader industrial level;
1. Power
Hydraulics are best for high-power applications. Their incompressible liquid medium has a high mass density, enabling hydraulic devices to generate higher pressures to flow power. Most industrial equipment operates at pressures ranging from 1,000 to 5,000 pounds per square inch (psi), and some hydraulic machines function at 10,000 psi or higher.
On the other hand, Pneumatic systems use gases with a low mass density that are easily compressible to multiple hundred psi. Thus, pneumatics are used in equipment that works between 80 and 100 psi. However, Pneumatics are not best for powering heavy machinery. Moreover, fluctuations in the compressed air can occur unexpectedly, resulting in unstable operation.
2. Sanitation
When we compare hydraulic and pneumatic systems in the sanitation fields, pneumatics always comes out on top due to its air leakage functionality. The compressed gases are purified from metal debris or water within the system. Eco-conscious companies use pneumatic systems for sustainable production methods.
Pneumatic applications, such as pharmaceutical labs and food industries, are also widely used in clean rooms. In these situations, hydraulic machines may cause pollution due to the leakage of water and oil through worn hoses or defective seals. However, using storage tanks and proper disposal of the residue may lower the risk of pollution caused by hydraulic machinery.
3. Speed
In speed terms, pneumatics is better than hydraulics as they have a higher compressed air flow rate. This system has a fast energy release ratio to move the actuators quickly. The fast air passage from the pipework has less mass density. Pneumatic actuators boost productivity by supporting higher duty cycles and faster cycle speeds. The quick movement of the cylinders is more useful, especially when the equipment is compact.
The valves and pneumatic cylinders can quickly shift their direction after releasing compressed air, so there is no need for additional disposal. On the other hand, hydraulic systems use water and oil and are slower than pneumatic systems. Hydraulic and mineral oils have higher resistance than air, and the oil’s viscosity causes the system to operate more slowly.
Hydraulic systems can create more force and pressure but are not as fast as pneumatic systems. Thus, they take more time to operate. The hydraulic fluid must be properly vented and redirected back into the tank in case of an emergency or leakage.
4. Energy
Regarding energy consumption, both systems depend on electrical power to operate. Pneumatic machines require the air compressor to run continuously for proper functioning. Furthermore, the air supply must be constantly replenished as it can’t be recycled, causing higher energy usage.
Additionally, energy is lost as heat during the compression process in pneumatic systems. However, there are several ways to improve the energy efficiency of your pneumatic applications. On the other hand, hydraulic systems can reuse the same fluid power after the initial startup. With an effective filtration system, hydraulics can operate more energy-efficiently.
5. Cost
Pneumatics are more cost-effective than hydraulic systems as they use less electricity to operate. Hydraulic equipment also has a longer lifespan than pneumatics. However, a central power supply can reduce the hydraulic system’s initial cost.
Read also: Directional control valves (DCVs) in pneumatic system