Introductions to What is Management Planning
Planning is the most basic of all what is management planning functions. There is no choice between planning and so planning. The Choice is only with regards to the method and techniques used to plan.
Most of us are planning many things in our day-to-day lives. Frequently, we plan to do official work, improve our careers, plan our investment, built own houses, do business and so on.
Organizations are so exception and lots of planning activities are done by the management people at all levels.
Planning is the process of selecting objectives and determining the course of action required so achieve these objectives. Lot of information has to be gathered and processed before planning is formulated.
Planning bridges the gap from where we are and where we want to go. It makes the things possible to occur which would not otherwise happen. Let us look all what the following observations suggest about principles of planning.
- Planning is outlining a future course of action in order to achieve an objective.
- Planning is looking ahead.
- Planning is getting ready to do something tomorrow
- Plan is a trap laid down to capture the future.
Let us now see some definitions of principles of planning.
According to Knootz and O’Donnell, “Planning is deciding in advance what to do. It is the selection among alternatives of future course of action for enterprise as a whole and each department within it. Plans involve selecting enterprise objectives and determining ways of achieving them”.
According to Terry, “Planning is the selecting and relating facts, and making and using of assumptions regarding the future in the visualization and formulation of proposed activities to be lived necessary to achieve desired results”.
The Haimann defines the planning as, “Planning is deciding in advance what is to be done. When a manager plans, be projects a course of action for the future, attempt to achieve e of a consistant, co-ordinates the structure of operations aimed at the desired results”.
In the words of Mary Cushing Niles, “Planning is the conscious of selecting and developing the best course of action to accomplish an objective. It is the basis from which future management action spring”.
Thus, the planning primarily focuses the future course of action i.e., what an action, how to take action and when to take action to achieve the desired goal. Planning leads to decision-making and controlling.
The Nature and Purpose of Planning
Nature of Planning
Define Planning in Management : On the basis of various definitions given above for planning, its various characteristics Planning-a primary or features can be identified as follows:
Planning- a primary functions:
Planning is the primary function of management and it precedes all functions, such as organizing, directing, controlling etc. There is no meaning of other activities without setting the goals to be achieved and line of action to be followed. In fact, all other functions of management largely depend on planning.
Planning-a dynamic process:
Planning is a continuous managerical function involving complex processes, such as perception, analysis, communication, decision and action. It is a never-ending activity of a manager of an enterprise.
Most of the plan are modifying, revising according to the changes in the circumstance. Moreover, a series of plans is to be followed successively one after the other.
Thus, the planning process will continue and will never come to an end.
Planning –based on objectives and policies:
Planning process involves setting of objectives to be achieved and determining the technique for achieving those objectives. The various techniques, such as policies, programs, procedures are formulated.
Objective determines where we are to go, and planning makes a bridge over where we are and where want to go. Thus, the planning and objectives are related.
Planning-a selective process:
For achieving a particular objective, there are number of alternative available. The planning manager has to select only one alternative which is best suited to the firm. Thus, planning a one kind of selective process.
Pervasiveness of planning:
Planning is generally considered as a function of top-level management, but it is not true. Planning function should spread or make available throughout the organization. Every manager has a planning function to perform.
Only, the scope of planning differs from person to person depending upon the levels of management.
Planning-an intellectual process:
Planning is a mental activity. It is a process where a number of activities are to be taken to decide the future course of action.
Various levels of managers have to consider various course of action, achieving the desired goals, the detailed process of every course of action and then finally decide which course of action may suit them best. Thus, planning is an intellectual action.
Planning is directed towards efficiently:
In general, all management functions including planning are directed to increase the efficiency of the firm.
Corollary of planning is (i) planning is an intellectual activity that aims the best way of doing things, and (ii) Planning provides the goals and objectives. Thus, planning is directed towards efficiency.
Planning-Focus with future activities:
Planning is primarily concerned with looking into future. It forecasts the future situation in which the organization has to function. Simply, planning decides the present what is to be done in future.
Flexibility of planning:
Planning is flexible as commitment which is based on future course of action. These are always dynamic. Therefore, an adjustment is needed between various factors and planning.
Planning is based on facts:
Planning is not a guesswork or trial and error method. It is conscious the determination of projecting a course of action for the future. Planning is based on facts, objectives and considered forecasts.
Importance of Planning or Objectives of Planning
Planning has a great importance in all types of organizations. Organisations often fail not because of lack of resources, but because of poor planning.
Planning has become a requisite for the survival and growth of business organization. It is necessary to plan due to the following reasons.
Primary of planning:
Planning is a primary function of an organization which proceeds all other functions. All other functions, such as organizing, staffing, directing and controlling are performed to achieve the objectives already set by planning process.
To achieve objectives:
Planning is directed towards the attainment of organization objectives. While planning, we should be clear about few questions.
- Why I am making this plan?
- What am I trying to accomplish?
- What resources do I need to execute the plan?
If we prepare answers for the above questions, it will provide a lot of clarity on objectives. Planning serves as a bridge between present and future objectives.
To cope with uncertainty and change:
There is a continuous change in the environment. A good organization has to work in accelerating change. This change is reflected in both tangible and intangible forms.
Tangible changes are in the form of changes in technology, market forces, government regulations etc. Intangible changes are in the form of changes in attitudes, values, cultures etc.
Planning enables the identification of future problems and meeting such contingencies. The planning helps to minimize risk while taking advantages of opportunities.
To facilitate control:
Control involves the measurement of accomplishment of events against plans and correction of deviations to assure the achievement of objectives as set by plans.
Planning provides the standards with which actual performance can be measured and corrective actions can be taken wherever necessary. Without planning, we do not know what to control.
To help in coordination – management planning
All the managerial functions lead to coordination in the organization. But real coordination begins with the planning stage. Since, all departments work in accordance with the overall plan, the harmony and coordination to be achieved. Coordination is the essence of management and planning is the base for it.
To increase organizational effectiveness:
The term effectiveness means that the organizations able to achieve its objectives within the given resources. A better planning ensures organizational effectiveness in many ways.
In better planning, all resources are put in a way that ensures their maximum efficiency and contribution to organizational objectives. Planning states the objectives of the organization in the context of given resources.
Therefore, each resource of the organization has a specific use at a particular time. Thus, planning ensures that resources are put into action in such a way that these have been specified.
To guide decision- making
Planning provides a basis for future oriented decisions. Without planning, business decisions may become random. Planning creates a better relation among various decisions. It serves as a framework for making rational decisions.
Principles of Planning Process
Planning is a process, therefore, it contain member of steps within it. It is not necessary that a particular planning process or steps are valid for all organizations and for all types of plans.
A planning process is suitable for large scale organization which may not be suitable for small organizations. Since, various factor that go into planning process may differ from plan to plan or form organization to organization.
The planning process or steps given here is mostly applicable for major programmes. But with minor modifications, the process is applicable for all types of plans.
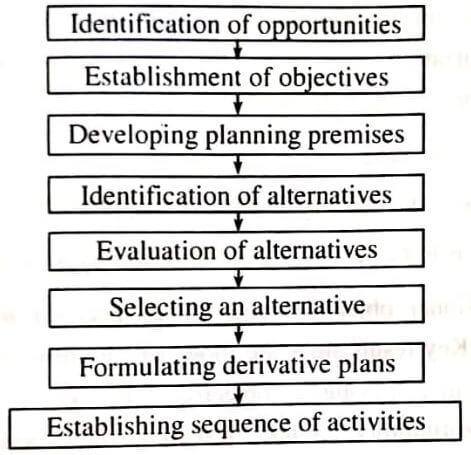
Identification of opportunities:
Identification of awareness of the opportunity is the starting point of planning. First of all, we should identify the possible future opportunities and analyses them clearly and completely.
From that, we should know:
- Where we stand,
- What is our strength and weakness,
- What problem we wish to solve and why, and
- What we expect to gain.
Formulation of derivative plans:
The derivative plans are formulated on the basis of the major plan. There are several minor plans required to support and execute the major plan. These plans are known as derivative plans.
The various derivative plans are planning for buying equipment, buying raw materials, recruiting and training personal, developing new product etc.
Establishing sequence of activities:
After formulating basic and derivative plans, the sequence of activities is determined so that plans are put into action while formulating derivative plans, a built-in mechanism should be created for periodic review and updating of various plans whenever necessary.
The starting and finishing times are fixed for each piece of work so as to indicate when and within what time that work is to be commenced and completed.
Types of Plans
Four major types of plans can help mangers achieve their organization’s goals:
- Operational plan
- Tactical plan
- Strategic plan
- Contingency plan
Operational plans lead to the achievement of tactical plans, which in turn lead to the attainment of strategic plans. In addition to these three types of plans, mangers should also develop a contingency plan in case their original plans fail.
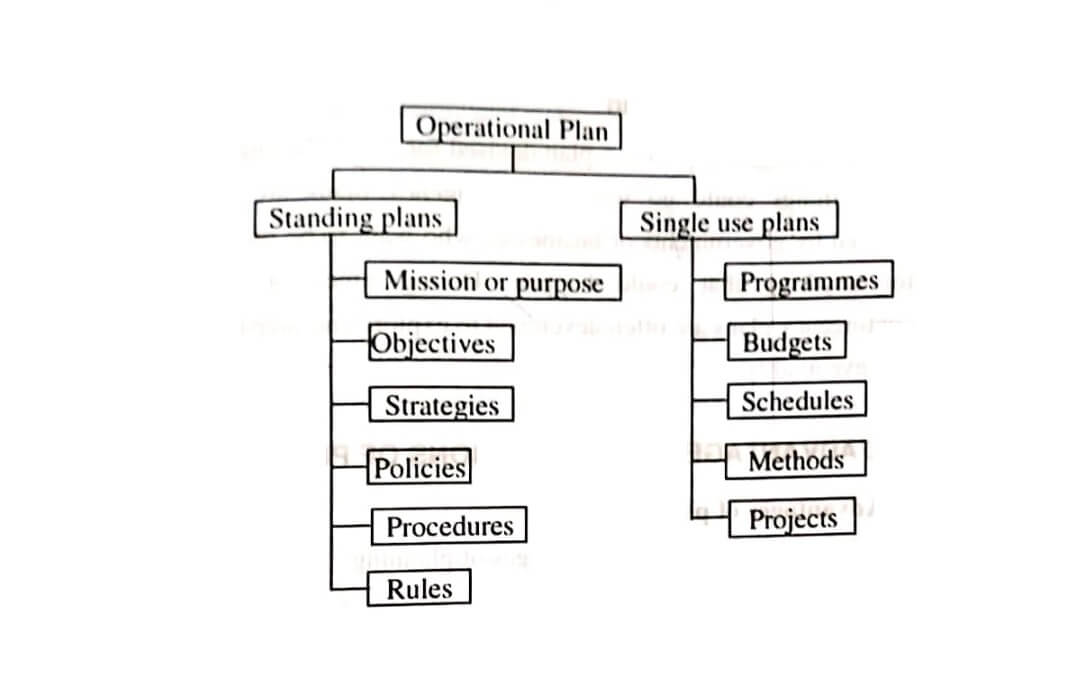
Operational Plan
An operational plan is one that a manager uses to accomplish his or her job responsibilities. Supervisors, team leaders, and facilitators develop operational plans to support tactical plans.
Operational plans can be a single-use plan or as on-going plan. Single-use plans apply to activities that do not recur or repeat. A one-time occurrence, such as a special sales program, is a single-use plan because it deals who, what, where, how and how much of an activity.
Standing or ongoing plans are usually made once and retain their value over a period of years while undergoing periodic revisions and updates.
Tactical plan
A tactical plan is concerned with what the lower level units within each division must do, how they must do it, and who is in-charge at each level. Tactics are the means needed to activate a strategy and make it work.
Tactical plans are concerned with shorter time frames and narrower scopes than are strategic plans. These plans usually span one year or less because they are considered shot-term goals.
Strategic Plan
A strategic plan is an outline of steps designed with the goals of the entire organization as a whole in mind, rather than with the goals of specific divisions or departments. Strategic planning begins with an organization’s mission.
Strategic plans look ahead over the next two, three, five, or even more years to move the organization from where it currently is to where it wants to be. Requiring multilevel involvement , these plans demand harmony among all levels of management within the organization.
Contingency plan
A contingency plan is a plan devised for a specific situation. When things could go wrong. Contingency plans are often devised by governments or businesses who want to be prepared for things that could happen. During times of crisis contingency plans are often developed to explore and prepare for any eventuality.
Advantages and Limitations of Management Planning
Advantages of planning
The following are the advantages of planning:
Helps in achieving objectives:
Planning concentrates more on setting goals or objectives of an organizations. It gives effective direction to the control of employees of the organizations towards achieving organizational goal.
Better utilization of resources:
Planning gives clear cut direction on what to produce and how to produce. Therefore, there is a possibility of utilizing the resources effectively.
Economy in operation:
Better utilization of resources leads to economy in operation.
Reduces uncertainty and risk:
Uncertain and change are inevitable, and planning cannot eliminate them. Planning enables the enterprise to make an adequate adjustment to adapt to future changes.
Improves competitive strength:
Planning enables a firm to remain in competition. Planning helps management to adopt modern methods of operation and to improve the quality of the product to attract the customer. Competitive strength is improved by adding these changes.
Effective control:
Planning serves as a base for control. Planning determines the time for starting and completing the projects, set standards of perfosrmance. It enables the managers to control the activities.
Coordination:
Planning enables effective coordination of all managerial functions. By providing well-defined objectives, unity of direction, well established policies, procedures and programmes, planning facilitates to get effective coordination.
Encourages Motivation:
A well prepared plan encourages the employee’s morale and confidence of the managers and also it gives them a sense of effective participation.
- See More : Controlling management and process
- See More : Management directing of principles
- See More : Organizing management of principles