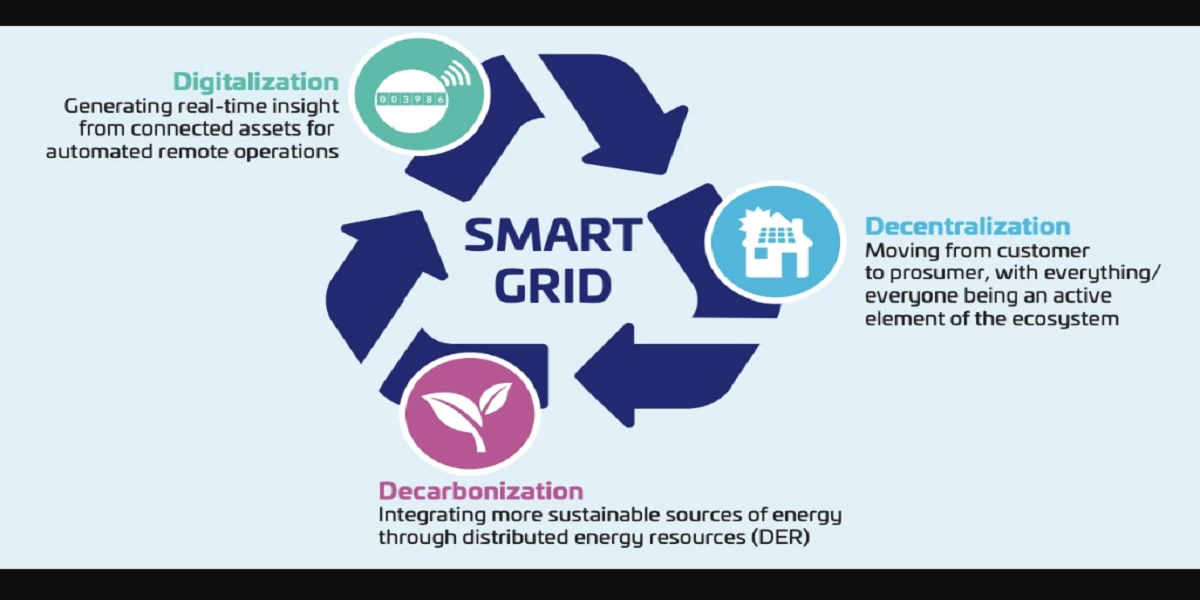
Think of your electricity grid like a smart network rather than a one-way highway. The smart grid is a next-generation version of our old-fashioned electricity grid, packed with technology that enables two-way interaction between electricity companies and consumers. It’s akin to upping your old landline to a smartphone—responsive, flexible, and considerably more efficient.
How It’s Different from Traditional Grids
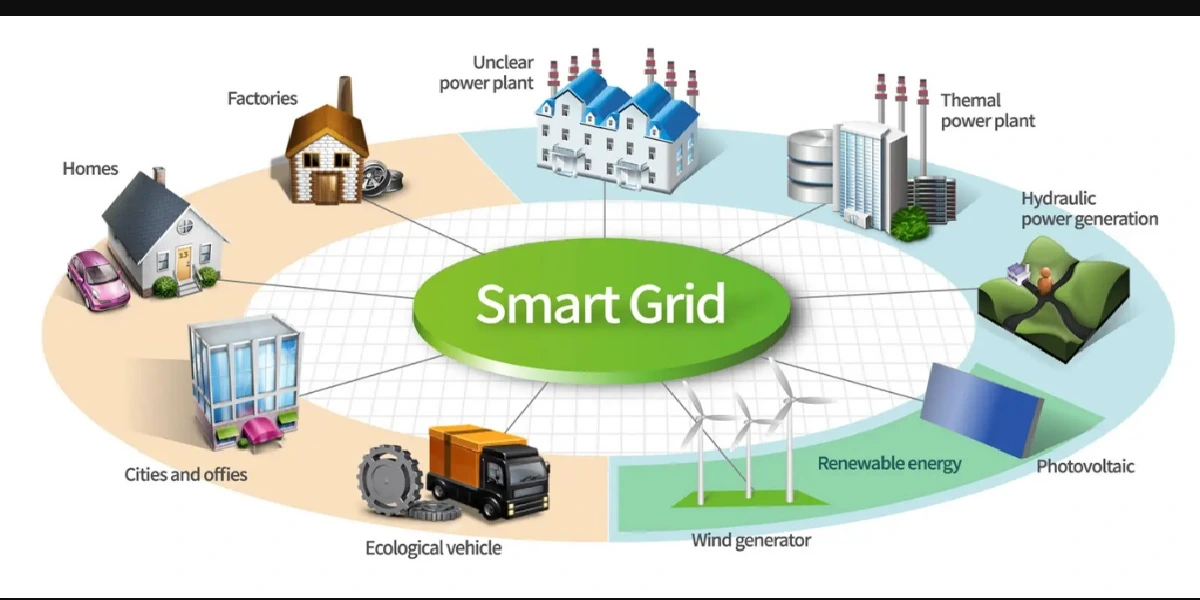
Old grids simply pushed power to your house. Smart grids respond, meter usage in real-time, manage power flow, and can even recommend ways to maximize your energy use. It’s all data, control, and flexibility.
Evolution of Power Systems
From Analog to Digital: The Grid’s Transformation
In the good old days, power grids were mechanical behemoths. No feedback loops, no data—just supply and hope for the best. With digitization, sensors and software have turned the grid into a responsive, data-driven system.
Why the Old Grid Isn’t Enough Anymore
Power outages, energy waste, and the growth of renewables have revealed the vulnerabilities in the old model. Smart grids tackle these problems by making power more reliable and sustainable.
Key Elements of the Smart Grid
Smart Meters
They are not your typical electric meters. They monitor your usage in real-time and provide it to you and your utility company. It’s like a Fitbit for electricity.
Advanced Sensors and IoT
Small sensors deployed over the network constantly keep an eye on health and efficiency. They’re the smart grid’s eyes and ears.
Communication Networks
Everything is connected by high-speed networks, providing instant data movement and decision-making.
How Smart Grids Work
Real-Time Monitoring and Automation
Smart grids recognize faults, redirect power, and keep systems going without the need for human intervention. They’re the energy system’s auto-pilot.
Data Flow and Decision Making
Information from homes, factories, and substations moves to centralized hubs where software makes incredibly quick decisions about how to deliver power effectively.
Why It Matters to You
Lower Energy Bills
Smart grids can reallocate energy consumption to off-peak times, saving you money automatically. It’s reverse Uber surge pricing.
Fewer Blackouts and Outages
Improved monitoring and predictive power, smart grids minimize outages and come back up more quickly when there are issues.
Cleaner, Greener Power
They make it easier to add solar, wind, and other renewables into the mix. That equals a smaller carbon footprint—no effort required.
Smart Homes and the Smart Grid
Connected Devices and Energy Efficiency
Your washing machine, fridge, and even your thermostat can all be set to run when energy is cheapest and cleanest.
Role of Renewable Energy at Home
Have rooftop solar? The smart grid can better manage it, sometimes even compensating you for excess energy returned to the system.
Benefits for Utility Companies
Predictive Maintenance
Utilities are able to repair issues before they become problems, cutting costs and downtime.
Load Balancing
Smart grids balance supply and demand on a see-saw basis—no place ever being overloaded or underpowered.
Smart Grid and Renewable Energy
Integration with Solar and Wind
Smart grids soak up variable renewable energy and level out the supply with real-time demand management.
Managing Energy Surplus
If there is surplus solar or wind energy, smart grids can spill it over to batteries or other sections that require it.
Conclusion: The smart grid is not a technology upgrade—it’s an upgrade to your lifestyle. It’s cost-saving, sustainable, and gets your energy experience smarter and smoother. You could be a homeowner, business owner, or just someone who flicks the switch on a lightbulb. The future of energy is calling—and it’s smart.
Read also: DC Generator Definition Working Principle EMF Types