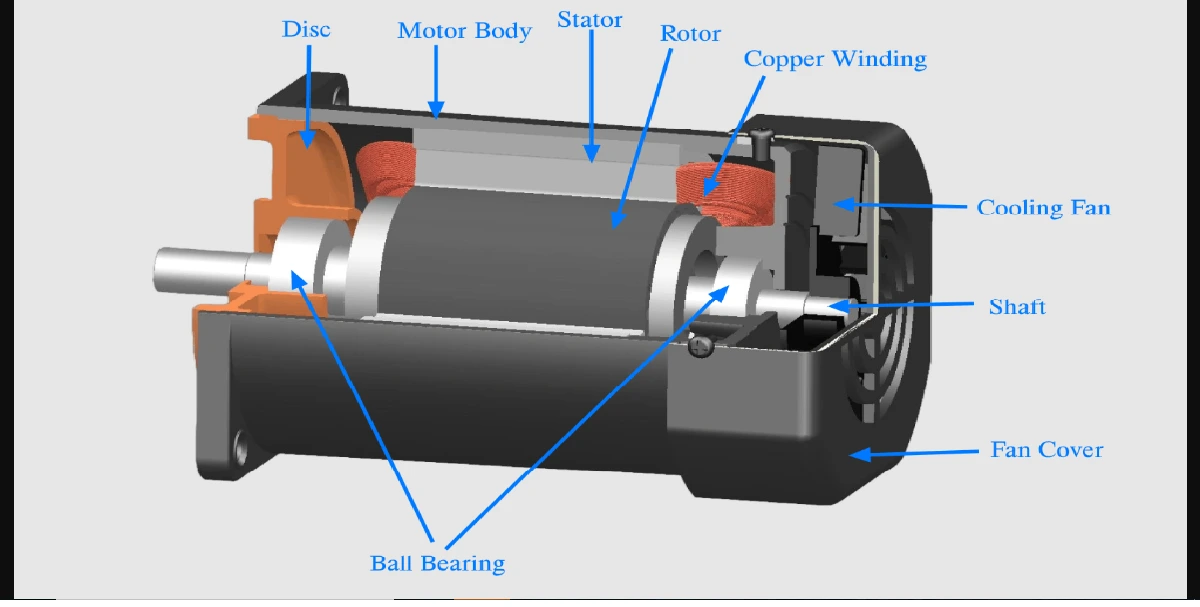
Repulsion motor are similar to series motors except that the rotor and the stator windings are inductively coupled, the rotor current is obtained by transformer action from the stator.
Types of Repulsion Motor
- Two stator winding repulsion motor
- Compensated repulsion motor.
- Repulsion start induction motors.
- Repulsion induction motors.
Repulsion Motor
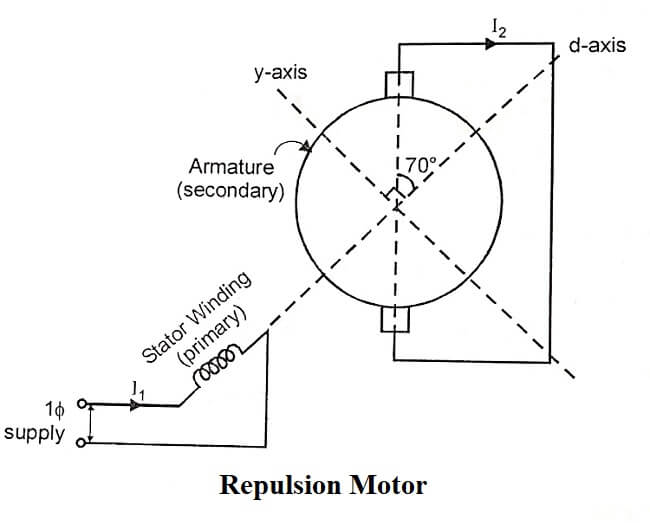
Repulsion motors is similar to de series motor with the rotor energized inductively. The single phase winding is placed in stator slots similar to the main winding of a single phase induction motor. The rotor consists of an oridinary distributed dc winding connected to the commutator at one end. The brushes are in touch with commutator and are short circuited to provide a closed current path. Figure shows a basic circuit diagram of a repulsion motor.
If the brushes are located in the d-axis, the emf in the effective armature winding will be maximum and so would be the short circuit current I2. Due to this, no torque will be produced and stator and rotor fields are aligned. If the brushes are located in the q-axis, the emf induced in the armature winding would add up to zero and current I2 is zero and hence no torque will be produced. As it is essential that both an armature current should flow and an angular displacement must exist between the two fields, the brushes are located in an intermediate position making a large angle of about 70° with the d-axis.
This appears like repulsion between the stator and rotor fields. That is why it is called repulsion motors. The direction of rotation of the motor will be reversed if the brushes are displaced on the other side of the q-axis.
Characteristics
Repulsion motors have characteristics similar to those of the series motors i.e. high starting torque and high no-load speed. The motor is a reversing type, and the direction may be changed during rotation.
Disadvantages
The draw-backs of repulsion motors are
- Speed variations with the variations in load dangerously high at no load.
- Low power factor, except at high speeds.
- Requires frequent maintenance.
- Higher cost.
- Sparking at the brushes.
- See More : Point to point links
- See More : Reactive power & voltage control
- See More : Methods of voltage control
[sc_fs_faq html=”true” headline=”h2″ img=”” question=”What is a repulsion motor?” img_alt=”” css_class=””] Repulsion motors are similar to series motors except that the rotor and the stator windings are inductively coupled, the rotor current is obtained by transformer action from the stator. [/sc_fs_faq]