Autonomic Nervous System has the following functions :
Reflex Activities : The ANS is involved in complex reflex activities that depend on sensory input to the CNS and on motor output. Reflex actions are rapid and are coordinated subconsciously in the brain, i.e., below the level of the cerebrum.
Deals with Excitation and Stressed Conditions : The sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves innervate most organs of the body. The effects of both these systems are opposite to each other such that a fine balance is maintained between them to ensure ideal functioning of all the organs. Sympathetic stimulation makes the body ready to deal with exciting and stressful situations, for example, strengthening of the defences in extreme temperatures and in danger. Therefore, sympathetic stimulation is recognised to mobilise the body for ‘fight or flight’ response.
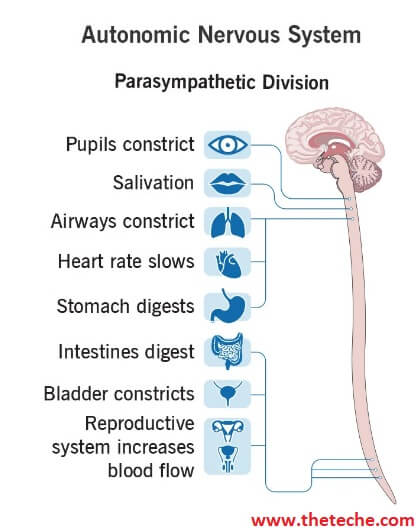
Slowing Down the Body Processes : Various significant processes of the body (except digestion and absorption of food and the genitourinary system) are slowed down by parasympathetic stimulation. The overall effect of parasympathetic stimulation is that of a ‘peacemaker’. It allows the processes of re-establishment quietly and peacefully.
Maintenance of Heartbeat : Usually, both the systems of the ANS work together and help in the maintenance of consistent heartbeats, normal temperature, and an internal environment in harmony with the immediate surroundings of the external environment.
| Read More Topics |
| Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic Nervous System |
| Transmembrane enzyme linked receptors |
| Factors affecting drug receptor interaction |
| Plasma protein binding of drug |





