Anti-inflammatory are drugs used to treat or reduces inflammation or swelling. Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are one of the most commonly prescribed drugs for pain and inflammation. NSAIDs are drugs with analgesic (pain reducing) antipyretic (fever reducing) and anti-inflammatory properties. NSAIDs are nonnarcotic (they do not induce stupor) which distinguishes it from. steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (Corticosteroids). Specific uses include the treatment of headaches, arthritis, sports injuries and menstrual cramps, acute pain and inflammation, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, spondylitis, painful shoulder, acute gouty arthritis and postoperative pain.
MECHANISM OF ACTION
> NSAIDs act by inhibiting the biosynthesis of prostaglandin, which is the basic cause behind fever, pain and inflammatory condition.
> The biosynthesis of prostaglandin is catalyzed by microsomal enzyme present in almost every mammalian cell type except erythrocytes.
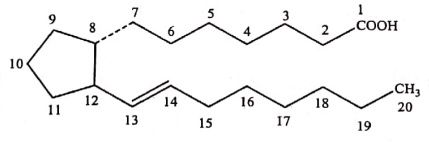
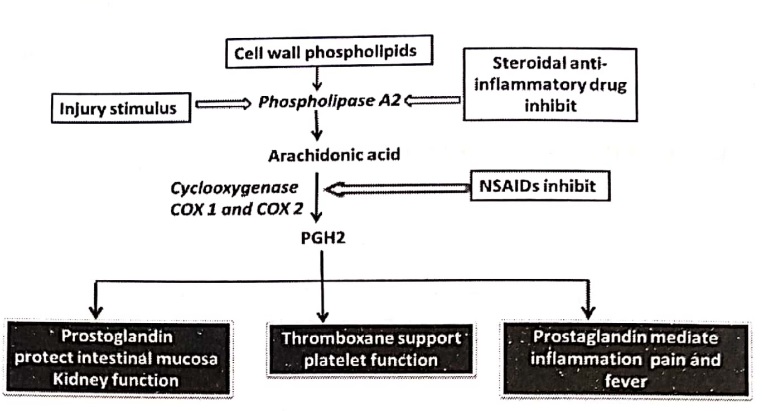
> Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids as a response to inflammation stimuli by the enzyme phospholipase A2.
> Prostoglandin (PGH2), prostacycline (PGI2) and thromboxane A2 (TxA2) are produced by arachidonic acid by cyclooxygenase (also known as prostaglandin synthase)
> Cyclooxygenase exist two isoforms COX 1 and COX 2.
> Cyclooxygenase 3(COX3 ) has been recently identified.
> COX 1 perform in physiological condition such as homeostatis of the entire organism, protect stomach from limiting acid secretion, renal function and platelet aggregation (promote blood clotting)
> COX 2 is generated during inflammation by pathological stimulus.
> Both COX enzymes produces prostaglandin that promote fever and pain.
> NSAID’s block COX enzyme and reduces the production of prostoglandin and also reduces inflammatory symptoms. Since prostaglandin that protect stomach and produce blood clotting is also reduced that block both COX 1 and COX 2 enzymes causes ulcers in stomach and increased risk of bleeding.
> Selective COX 2 inhibitors may eliminate side effects associated with NSAID’S due to COX 1 inhibition such as gastric and renal effect.
> Many COX 2 specific inhibitors have been removed from the market due to its significant increase in heart attack and stroke.
| Read More Topics |
| Synthetic cholinergic blocking agents |
| Introduction of sympathomimetic agents |
| Biosynthesis and catabolism of acetylcholine |





