A beam is a rod of uniform cross section of an elastic materials, whose length is much greater as compared to its thickness and breadth.
The beams are usually set in horizontal position and are designed to support heavy loads. They can support heavy loads such as roofs in buildings and heavy vehicles passing over the bridges.
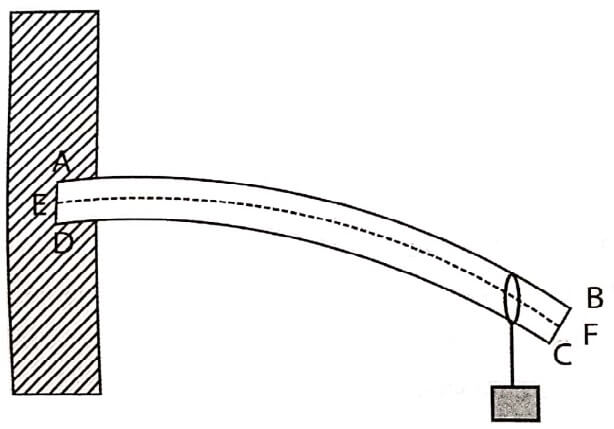
A beam which is clamped at one end and loaded at the other end is called cantilever.
In order to study the bending of beams the following assumptions are made
The bending of beam occurs when one end of the beam is fixed and other end is loaded with different weights.
Longitudinal filaments
A beam is regarded as made up of a number of thin layers placed in contact parallel to one another. Further each layer is regarded as a collection of thin layers parallel to the length of the beam. These fibres are called longitudinal filaments.
Neutral surface or neutral filament
Neutral axis
The intersection of the neutral surface by the plane of bending is called the neutral axis.
Plane of bending
The plane in which the bending of the beam takes place is called the plane of bending.
Axis of bending
The line perpendicular to the plane of bending on which the centre of curvature of all bent filament lie is called axis of bending.
| Read More Topics |
| Energy distribution of electrons in metals |
| Fibre optic sensor working principle |
| Industrial applications laser welding |





