Figure shows evolution of brushless dc motor.

Conventional DC Motor
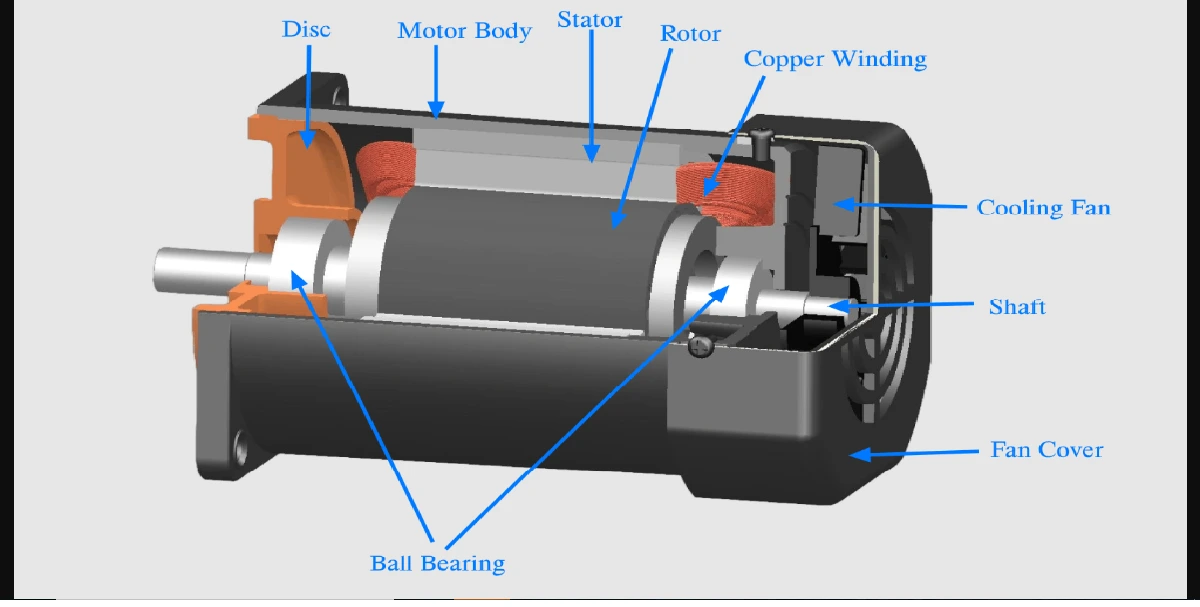
The first stage of evolution of DC motor is conventional type DC motor. It is an electro magnetic and electro dynamic equipment.
Sator
Stator is made up of forced steel with inward projected poles. The poles carrying field windings. The field windings are connected such that the current passing through it sets up a magnetic field in the airgap. The ends of the field windings are connected to field winding terminals.

Rotor
The rotor is made up of silicon steel stampings with slots in its exterior surface. The slots are accommodating the closed armature windings wound for the same number of poles as the stator.
The armature winding is connected suitably to various segments of the commutator mounted on the shaft. Carbon or graphite brushes, sliding contacts over the commutator of magnetic neutral plane or interpolar axis. Brushes are connected to the terminals of armature.
Advantages
- It is on load and no load speeds can be controlled
- Regenerative braking is possible
- Standardized design procedures are available.
Disadvantages
- Globally available electric supply is 3 -phase ac of fixed frequency. A rectifier is required for getting de supply to run the motor.
- It requires a regular maintenance because of sliding contacts between the commutators and brushes.
- Here armature is in the rotor, so special ventilation arrangements are to be made for effective cooling.
- Maximum operating armature voltage is limited, because of the sliding contacts. Sliding contacts between brushes and commutator generates electromagnetic waves which cause undesirable interference with communication systems.
Permanent Magnet DC Motor (Second Stage of Evolution of DC Motor)
The seconds stage of development of de motor is permanent magnet dc motor. The construction of PMDC motor is similar to the conventional de motor, with the following differences. Stator poles are replaced by suitable permanent magnets. No. need to have field windings.
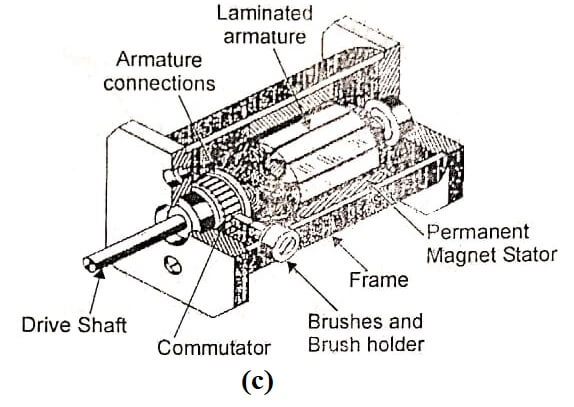
Advantages
- There is no field winding and so there is no field copper-loss.
- Efficiency is higher.
- Size is small.
Disadvantages
- Airgap flux cannot be controlled
- Large size permanent magnets are used
- Motor power rating is restricted.
Brushless Permanent Magnet DC Motor (Third Stage of Evolution of DC Motor)
Stator: The stator of the PMBLDC motor is made up of silicon steel stampings with slots in its interior surface. These slots are accommodated either in closed or open distributed armature winding.
This winding is to be wound for a specified number of poles (even number). This winding is suitably connected to DC supply-through a power electronic switching circuits.
Rotor: Rotor accommodates a permanent magnet. The number of poles of the rotor is same as that of stator. The rotor shaft carries a rotor position sensor. A position sensor provides information about the position of the shaft at any instant to the controller which sends signals to the electronic commutator.

Advantages of PMBL DC Motor
- There is no field winding so that field copper loss is neglected.
- Length of the motor is very small as there is no mechanical commutator, so that. size becomes very small.
- Better ventilation because of armature accommodated in the stator
- Regenerative braking is possible.
- Speed can be easily controllable.
- Motor can be designed for higher voltages subjected to the constraint caused by the power semi conductor switching circuit.
- It is possible to have very high speeds.
Disadvantages
- Motor field cannot be controlled.
- Power rating is restricted because of the maximum available size of permanent magnets.
- It requires a rotor position sensor.
- It requires a power semi conductor switching circuit.
Applications
- Automotive applications
- Veticular electric drive motors
- Applications in textile and glass industries
- Computer and Robotics
- Small appliances such as fans, mixers etc.
[sc_fs_faq html=”true” headline=”h2″ img=”” question=”What is permanent magnet DC commutator motor?” img_alt=”” css_class=””] A DC motor of permanent magnet in the stator and armature winding, commutator in the rotor. This motor is called permanent magnet DC commutator motor. [/sc_fs_faq]
| Read More Topics |
| Three phase induction motor |
| Whirling or critical speed of shafts |
| Gyroscopic effect on naval ship |