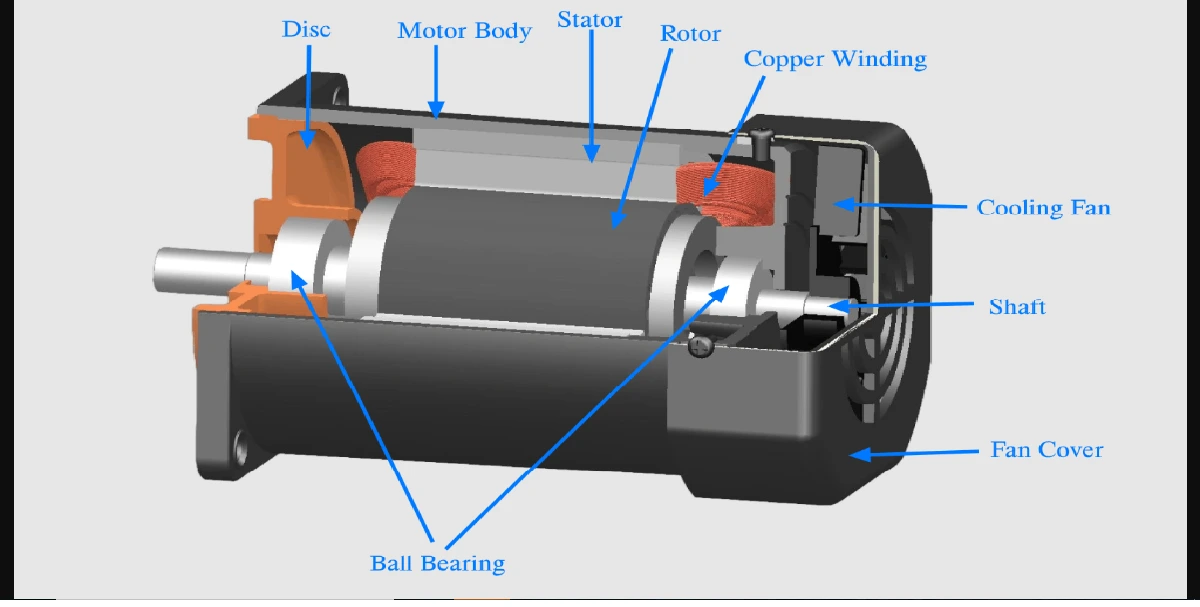
Whenever an electric drive is disconnected from the supply, the speed of the driving motor gradually decreases and becomes zero. Braking is a generic term used to describe a set of operating conditions for electric drive systems. It includes rapid stopping of the electric motor, holding the motor shaft to a specific position, maintaining the speed to a desired value of preventing the motor from over speeding.
During the braking process, the energy can change its flow between the source and load. In this period, the machine act as a generator, which pumps the energy back to the electric supply. The complete operational cycle of an electric drive system is highly dependent on braking method. The quickness and accuracy of braking techniques often determine the productivity and quality of the manufactured goods. Generally there are two types of braking methods namely
- Mechanical braking
- Electric braking
For both methods of braking, the braking torque is required.
Mechanical braking
In mechanical braking, the frictional force between the rotating parts and brake drums provide the required brake. Mechanical equipments such as brake linings, brake shoes and brake drums are required. This type of braking require frequent maintenance.
[sc_fs_faq html=”true” headline=”h2″ img=”” question=”What is meant by mechanical braking?” img_alt=”” css_class=””] In mechanical braking, the frictional force between the rotating parts and brake drums provide the required brake. [/sc_fs_faq]
Electric braking
In electric braking, the motor is made to work as generator. So it produces a negative slip and negative torque (braking torque). This is achieved by suitably changing the electrical connections of the motor. Whether mechanical or electric braking, the braking, of the drive should be such as to stop the motor at the specified point of time and location, for reasons of safety. The electric braking may be required due to the following reasons.
- If a motor running at some speed is disconnected from the input supply, the only opposing torque will be the load torque. The motor will stop only after the kinetic energy stored in its inertia is dissipated. When either the load torque is small or the inertia is large, the motor takes long time to stop. In applications requiring frequent stops, the stopping time must be decreased by introducing additional opposing torque by use of electric braking.
- In some important applications such as traction, rapid emergency stops are essential to prevent accidents. The electric braking is mainly used to achieving quick and very smooth stops.
- In certain applications involving active loads, the drive speed will reach dangerous values if the braking force is not provided by the motor. For example, in a hoist application when a loaded hoist is being lowered, the motor should provide a braking force (braking torque) to hold the speed within safe limit. In the same way in electric traction, when a train goes down a steep gradient, a braking force is required to hold the train speed within safe limits.
- In certain applications involving active loads, the drive speed will reach dangerous values if the braking force is not provided by the motor. For example, in a hoist application when a loaded hoist is being lowered, the motor should provide a braking force (braking torque) to hold the speed within safe limit. In the same way in electric traction, when a train goes down a steep gradient, a braking force is required to hold the train speed within safe limits.
Compare Electrical and Mechanical Braking
| Mechanical Braking | Electrical Braking |
| Low efficient | High efficient method. |
| The energy of the rotating parts is wasted as heat in friction. | The energy of the rotating parts can be converted to electrical energy which can be utilized or returned to the supply mains. |
| It require frequent maintenance like adjustment of brakes, replacement of brake linings. They are prone to tear & wear. | It require very little maintenance because of absence of mechanical equipments. |
| Depending upon the conditions the braking may not be very smooth. | Braking is very smooth, without snatching. |
| This braking is applied to hold the system at any position. | It cannot produce holding torque. It requires electrical energy for operation. |
| Brake drum, brake shoes and brake linings are needed. | Equipment of higher rating than the motor rating may. be needed in certain types of braking. |
Compared to the mechanical braking, electric braking is highly efficient and requires low maintenance. Nevertheless, braking can result in stressful electrical and mechanical transients. Therefore, the braking system must be designed to ensure effective and safe operation.
| Read More Topics |
| Characteristics of DC Generator |
| Speed control of DC shunt motor |
| Gyroscopic effect on ship |
| Different types of electrical braking |