A cell is a device for the conversion of electrical energy into chemical change or vice versa.
It is a system containing two metallic electrodes, dipped into the same or different electrolytes, connected by an external metallic conductor.
Types of cells
The cells are classified into two types:
- Electrolytic cells.
- Electrochemical cells.
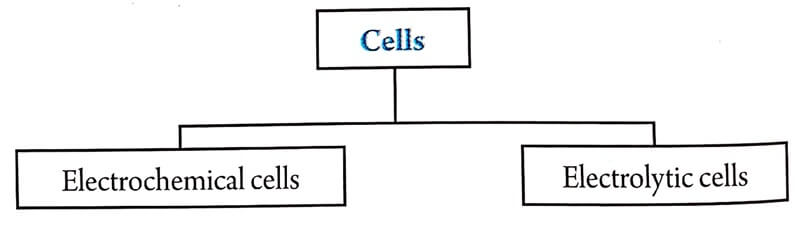
Electrolytic cells
These are cells in which electrical energy is converted intro chemical reaction.
Eg., electrolysis of an aqueous solution.
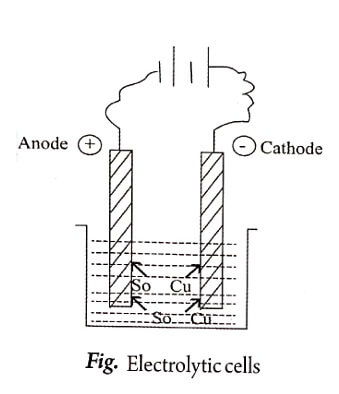
Electrochemical cells
These are cells in which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy due to the chemical change.
Eg., daniel cell.
Difference Between Electrolytic Cells and Electrochemical Cells
| S.No | Electrolytic cell | Electrochemical cell |
| 1 | It is a device in which chemical reactions are brought about by a passage of electric current. | It is a device in which a chemical reaction is utilised to get electrical energy. |
| 2 | It converts electrical energy into chemical energy. | It converts chemical energy into electrical energy. |
| 3 | In this type of cell, negative electrode is cathode and positive electrode is anode. | In this type of cell negative electrode is anode and positive electrode is cathode. |
| 4 | E.g., electrolysis of an aqueous solution of HCl into H2 and Cl2 | E.g., Daniel cell, fuel cell etc. |
| 5 | In this cell, the electrodes may be of same or different materials. | In electrochemical cell, the electrodes are of different materials. |
| 6 | No salt bridge is required. | A salt bridge is required. |
| 7 | Amount of electricity required for carrying out electrolysis is measured by coulometer. | emf of this cell in measured by voltmeter or potentiometer. |
[sc_fs_faq html=”true” headline=”h2″ img=”” question=”How do electrolytic cells work?” img_alt=”” css_class=””] Electrolytic cells use electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous chemical reactions, forcing ions to migrate towards opposite electrodes where reduction and oxidation occur. [/sc_fs_faq]
| Read More Topics |
| Introduction of electrochemistry |
| Types of softening of water processes |
| Requirement of boiler feed water |





