Directional Control Valves (DCVs)
The primary function of any control valve is to direct, regulate the flow of fluid and regulate the pressure in various loading devices. Usually, directional control valves are used for sensing, processing, controlling which involves in the following functions.
- Controlling the flow by guiding and directing It to a loading line.
- Select the path air takes through the system or cancelling the signal in blocking its path.
- Generating or making alert the signal.
- Releasing the air to atmosphere or return the fluid to reservoir.
- Performing logic control functions
- Stopping and starting air flow (on-off valves).
- Sensing cylinder positions (limit valves).
In hydraulic systems, valves are classified into the following types
- Directional control valves
- Non return valves
- Flow control valves
- Pressure control valves
- Solenoid valves.
Directional control valves (DCVs) are one of the most fundamental parts in pneumatic and hydraulic systems. Directional control valves are designed to direct the flow of fluid, at the desired time, to the point in a fluid power system where it will do work. They usually consist of a piston inside a cylinder which is electrically controlled. The movement of the cylinder restricts or permits the flow, thus it control the fluid flow. Directional control valves for hydraulic and pneumatic systems are similar in design and operation. However, there is one major difference. The return port of a hydraulic valve is ported through a return line to the reservoir, while the similar port of a pneumatic valve is usually line to the reservoir, while the similar port of a pneumatic valve is usually vented to the atmosphere. There are two common forms of DCVs.
- Sliding spool valve
- Rotary spool valve
- Poppet valve
Sliding Spool valve – Directional Control Values
Sliding spool valve consists of a spool inside a cast iron or steel housing. The spool slides to different position in the housing and route the fluid based on the spool’s position. The sliding element is also referred to as a piston. For valves with more ports, the spool is designed with more pistons or lands on a common shaft.
When the spool is moved to the right direction. (a) the inlet (pressure supply) and outlet ports are open and exhaust port is closed. Therefore the actuator is pressurized and activated. When the spool is moved to the left direction. (b) the inlet port is closed and outlet and exhaust ports is open. Therefore the actuator is deactivated. The spool position may be actuated by mechanical levers, hydraulic pilot pressure, or solenoids which push the spool left or right. In this illustration solenoid is used to activated the valve.
Advantages of sliding spool valve
- Very flexible as regards porting configuration
- Relatively straight forward manufacture
- Low inertia giving good acceleration and deceleration
- Low operating load.
Disadvantages of sliding spool valve
- Necessity for precision manufacture increases with increasing pressure
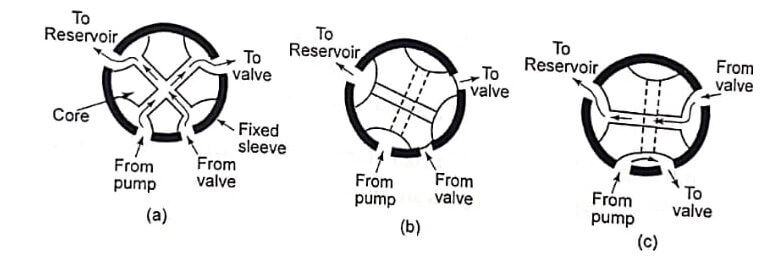
- Rotary Spool valve
The rotary spool directional control valve has a round core with one or more passages or recesses in it. The core is mounted within a stationary sleeve. As the core is rotated within the stationary sleeve, the passages or recesses connect or block the pots in the sleeve. The ports in the sleeve are connected to the appropriate lines of the fluid system. The operation of a rotary spool valve. (a) and (c) show the valve in a position to deliver fluid to another valve, while the valve in the neutral position, with all passages through the valve blocked.
Advantages of rotary spool valve
- Good flexibility as regards porting configuration
- Generally suitable for low-cost production with simple porting
- High flow rate for given size
Disadvantages of rotary spool valve
- May be limited in processing rating
- Manufacturing cost increases with increasing complexity of porting
- Poppet valve
The valve consist of a movable poppet which closes against the valve seat by the spring force. In the closed position, fluid pressure on the inlet side tends to hold the valve tightly closed. A small amount of movement from a force applied to the push button opens the poppet and allows fluid to flow through the outlet of the valve.
Advantages of poppet valve
- High response
- Low leakage
- Easy to manufacture with high pressure rating
- Low cost
- Generally intensive to contaminants
Disadvantages of popper valve
- Strictly limited design flexibility i.e. each valve is only capable of two-way function
| Read More Topics |
| Precessional angular motion |
| Gyroscopic effect on naval ship |
| Four types of vibration |